Condition Builder
The Condition Builder allows you to construct conditional statements within your workflow. It can be used to control the flow by utilizing the Condition or Conditional Loop nodes. You can add a condition node by clicking the Add Condition button.
Change Condition Name
You can change the name of a condition to better understand what it is processing.

Condition Type
In addition to comparing a single condition, you can add multiple conditions in the following forms:
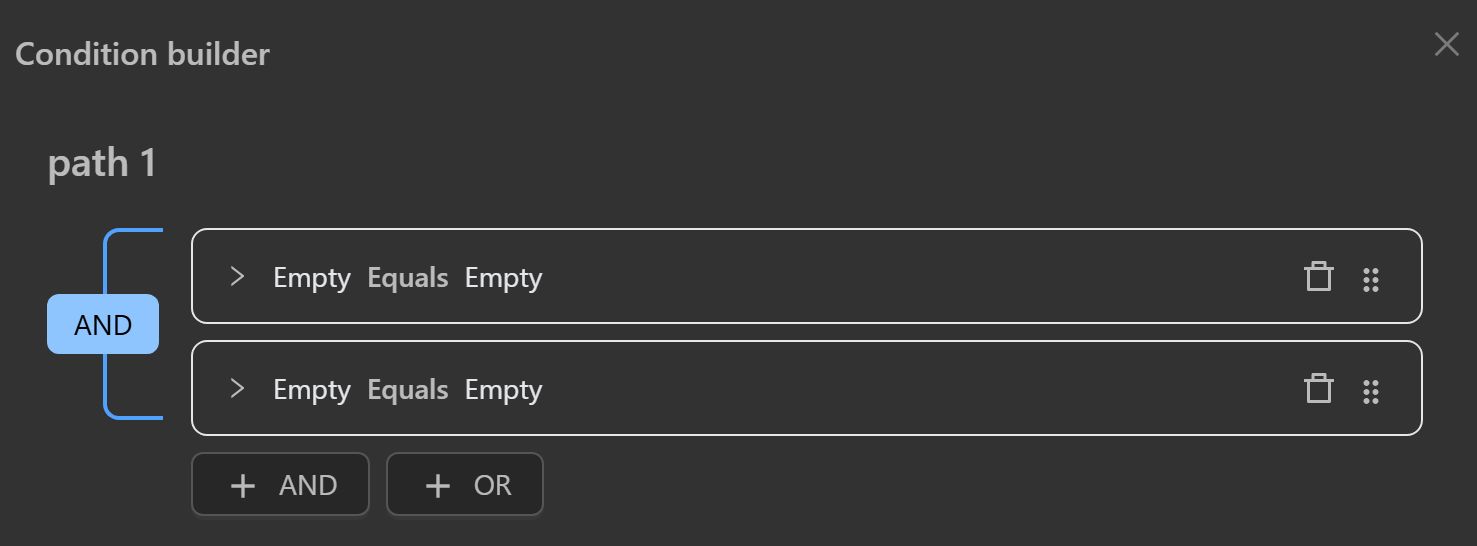
AND
All specified conditions must be satisfied for the node connected to the next output path to execute.
To add conditions to be checked together, you click the AND button, creating a branch condition that connects to the previous condition as follows:

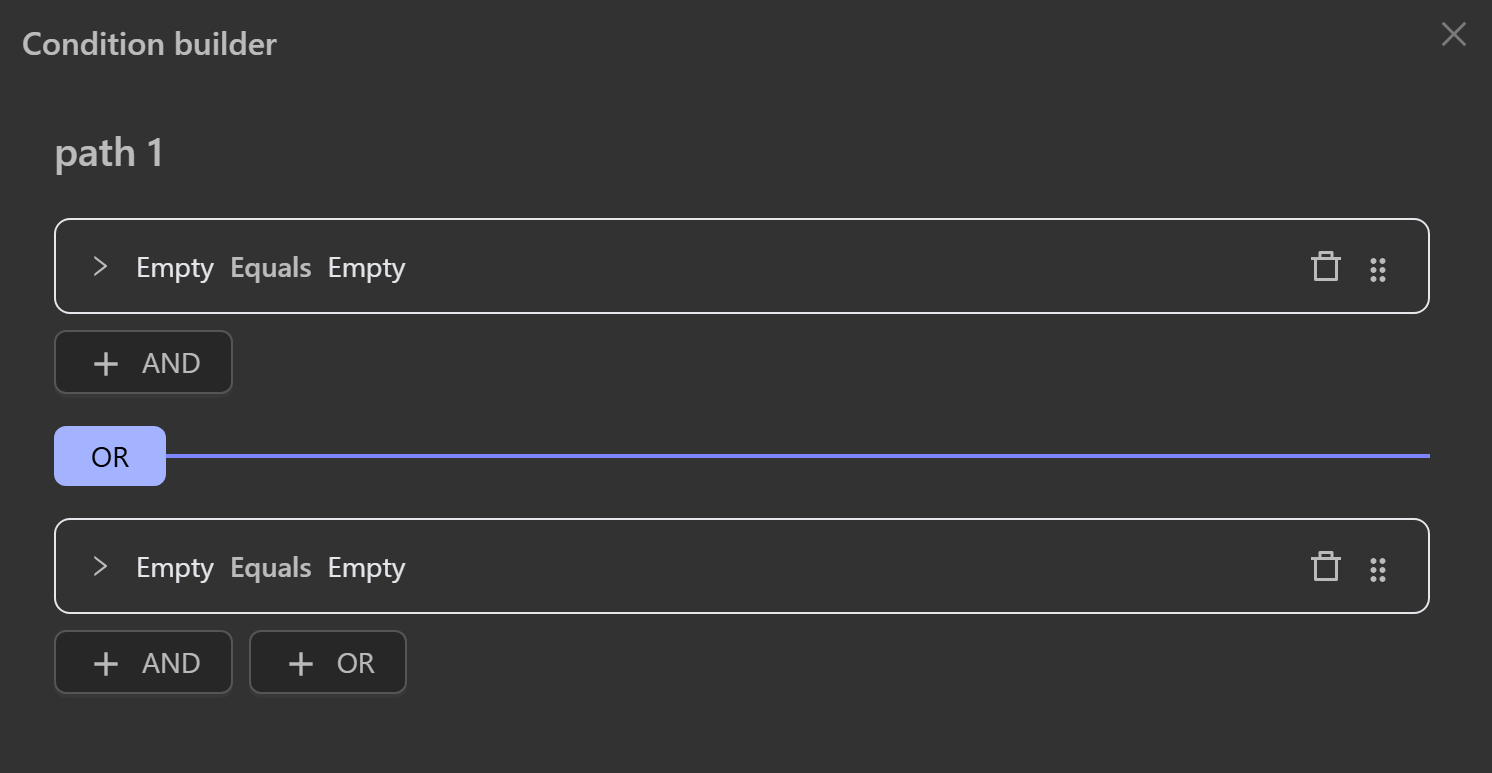
OR
At least one of the specified conditions must be satisfied for the node connected to the next output path to execute.
To add conditions to be checked independently, you click the OR button, creating a branch condition that connects to the previous condition as follows:

Comparison Data Type
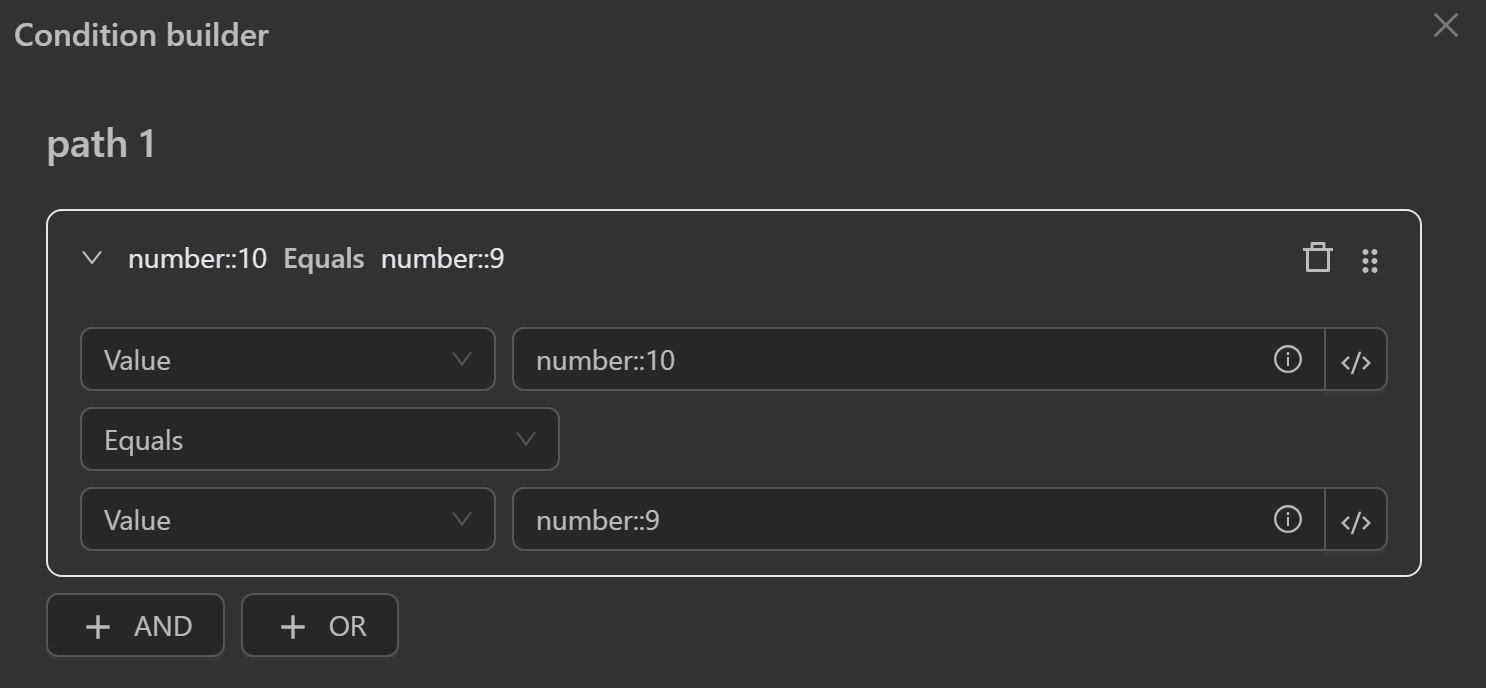
Value
For the value, you want to compare, you can write an expression in the text field.
- Value: Common value types such as text, numbers, etc.
- Value Prefix: This prefix is a convention to indicate the data type of a value. It can be used to convert a value to the corresponding data type. For example, the
string::prefix can convert a value to a string, andnumber::can convert a value to a number. You can add the following prefixes:string::: Converts the value to a string.json::: Converts the value to JSON.number::: Converts the value to a number.boolean::: Converts the value to a boolean.
- Value Prefix: This prefix is a convention to indicate the data type of a value. It can be used to convert a value to the corresponding data type. For example, the
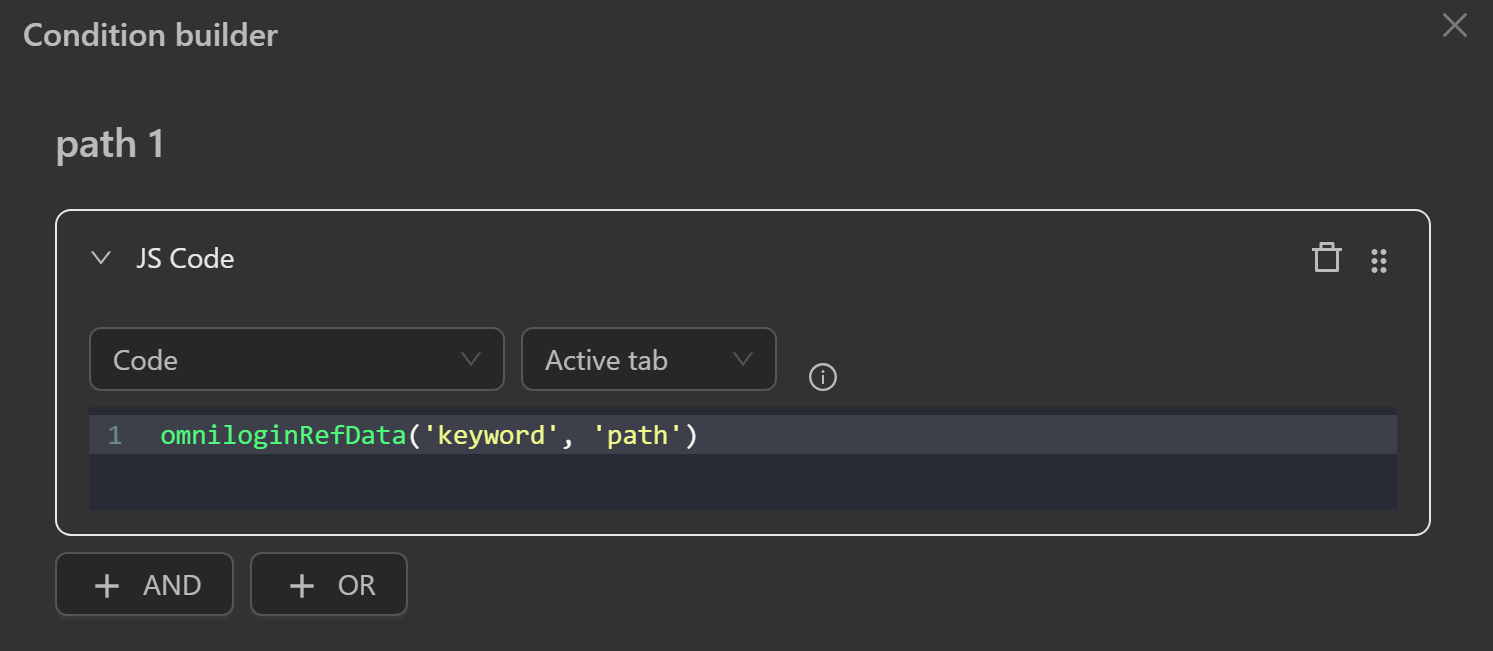
- Code: A JavaScript expression.
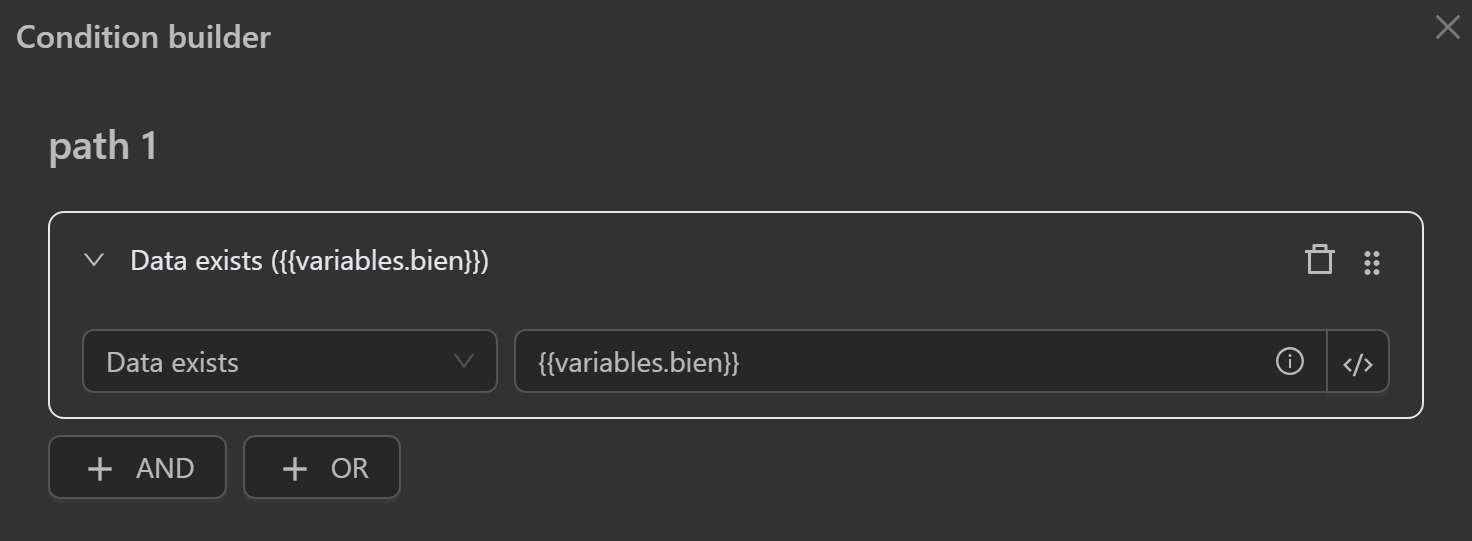
- Data Exists: Checks if process data (variables, tables, etc.) exists.
Element
Use a selector to retrieve the CSS selector or XPath of an element.
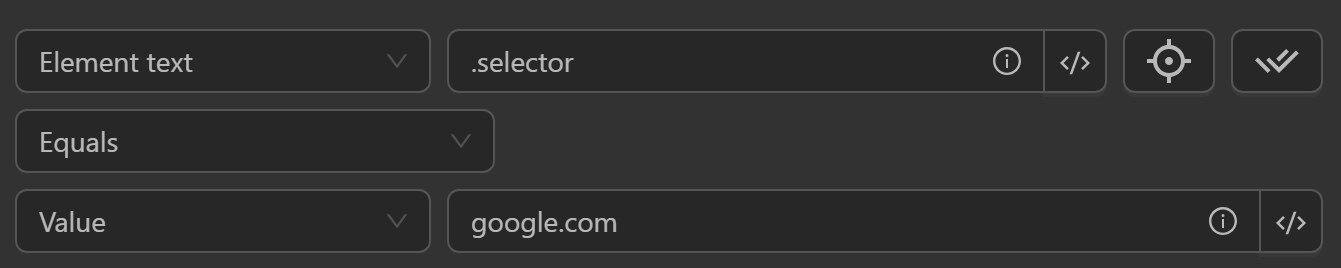
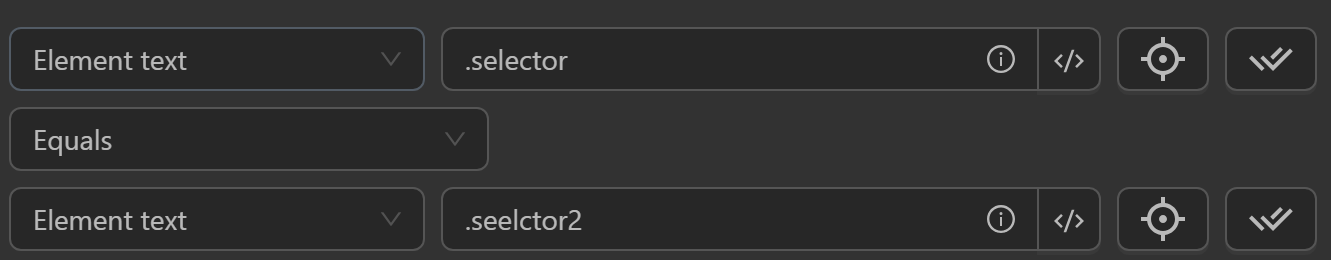
Element Text
- Compare an element's text based on its CSS selector or XPath.
- Compare with: value, element text, element attribute value.
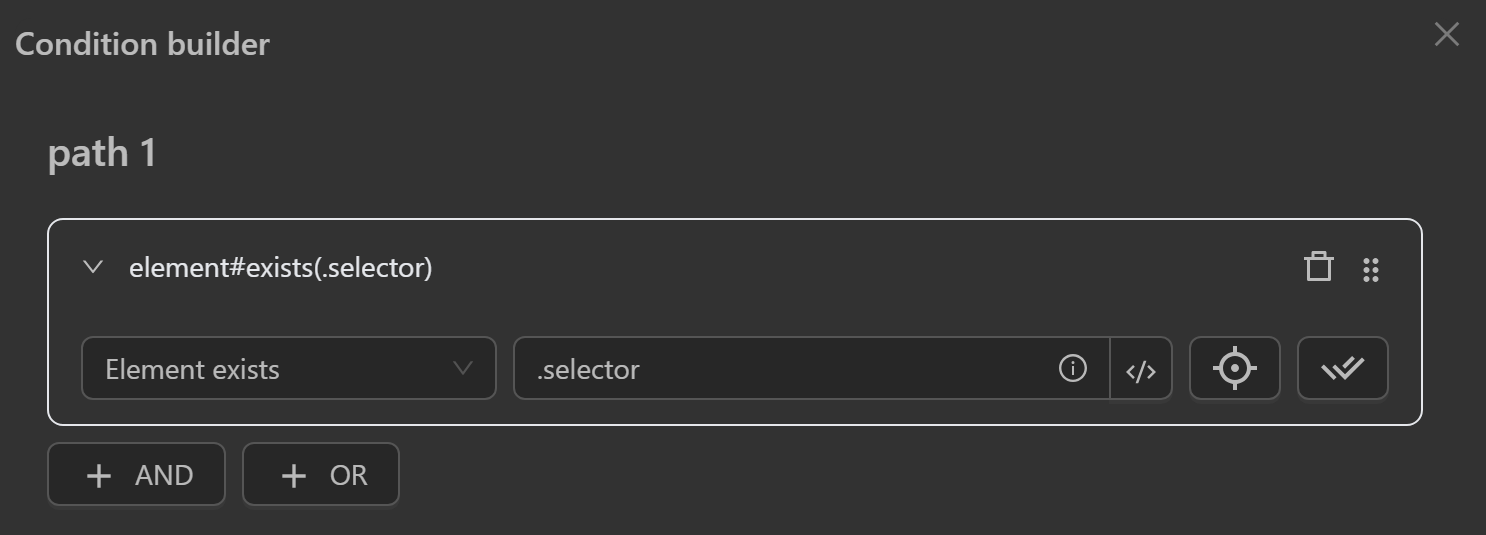
Element Exists
- Check if an element
existsvia its CSS selector or XPath.
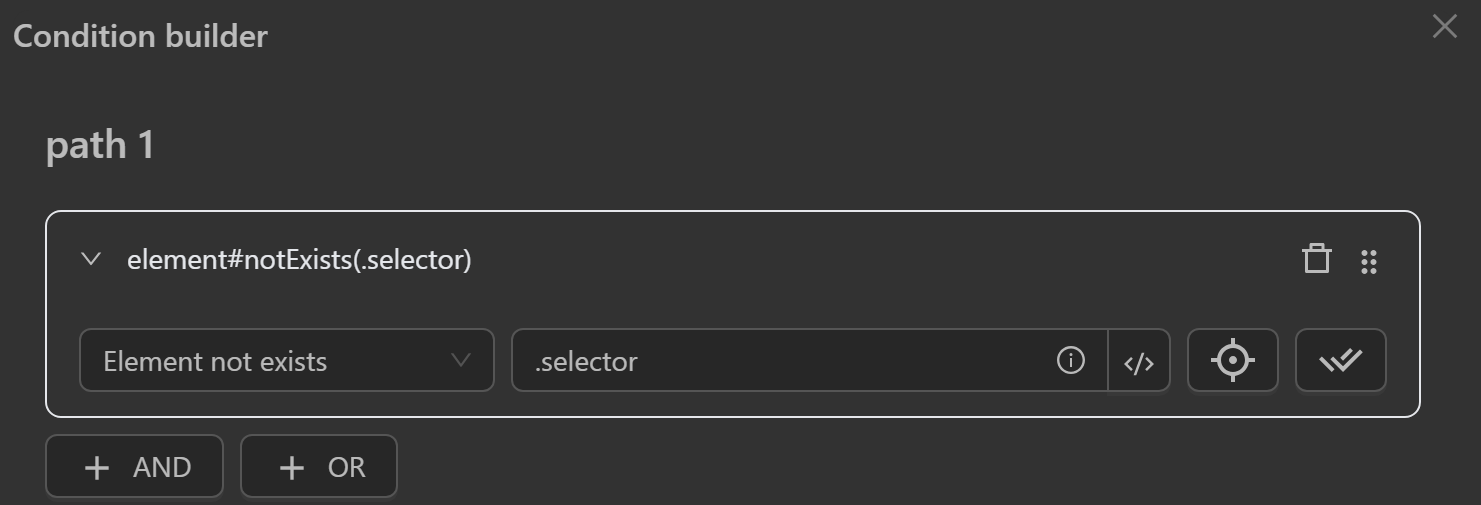
Element Not Exists
- Check if an element
does not existvia its CSS selector or XPath.
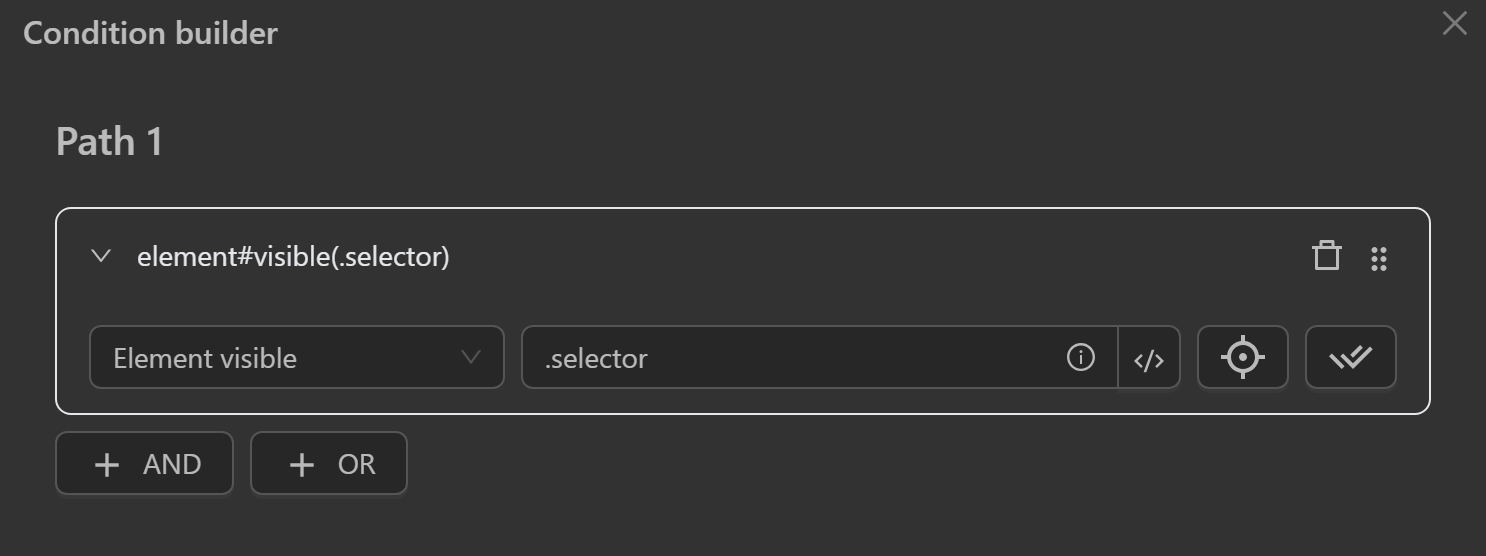
Element Visible
- Check if an element
is visiblevia its CSS selector or XPath.
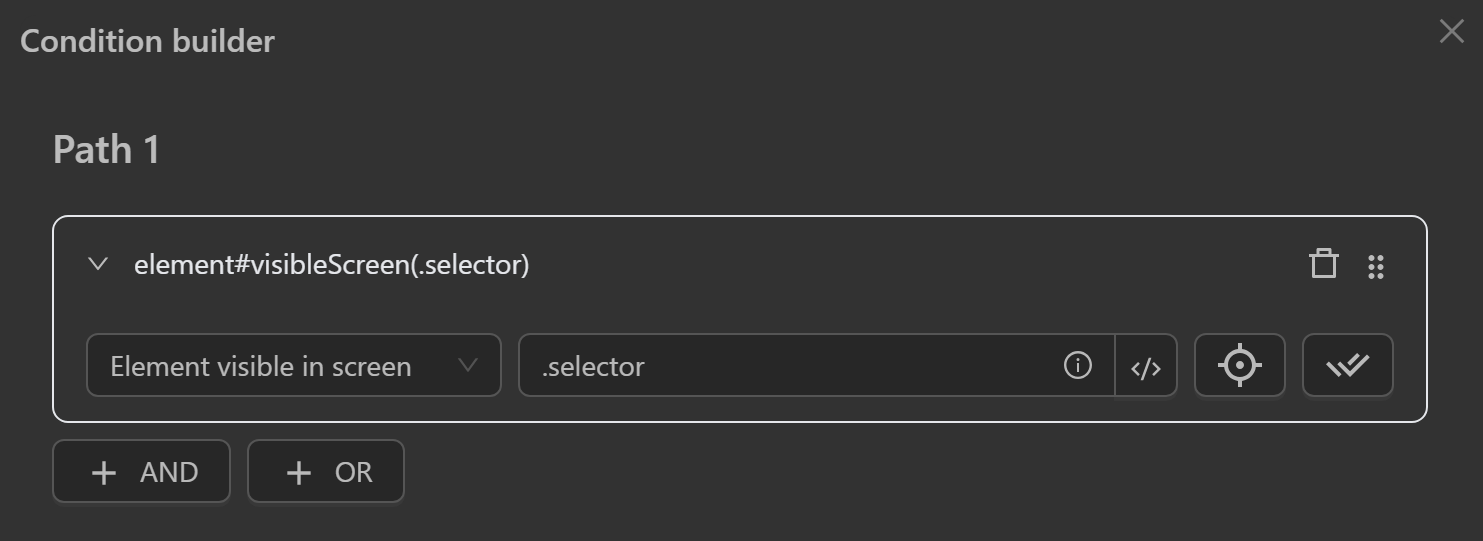
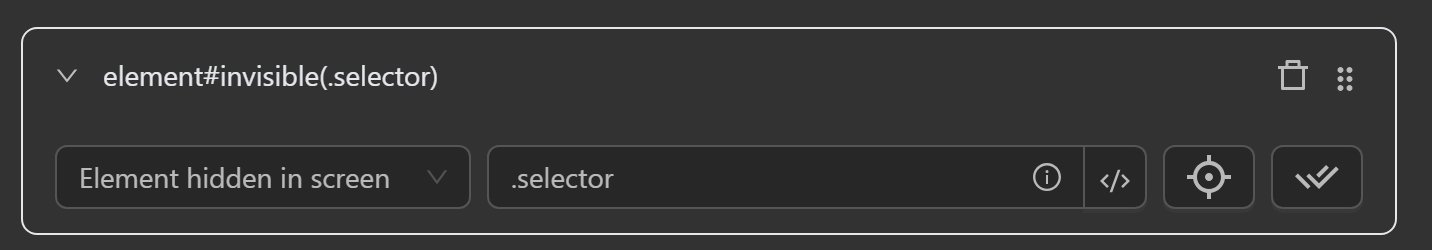
Element Visible in Screen
- Check if an element
is visible on screenvia its CSS selector or XPath.
Element Hidden in Screen
- Check if an element
is not visible on screenvia its CSS selector or XPath.
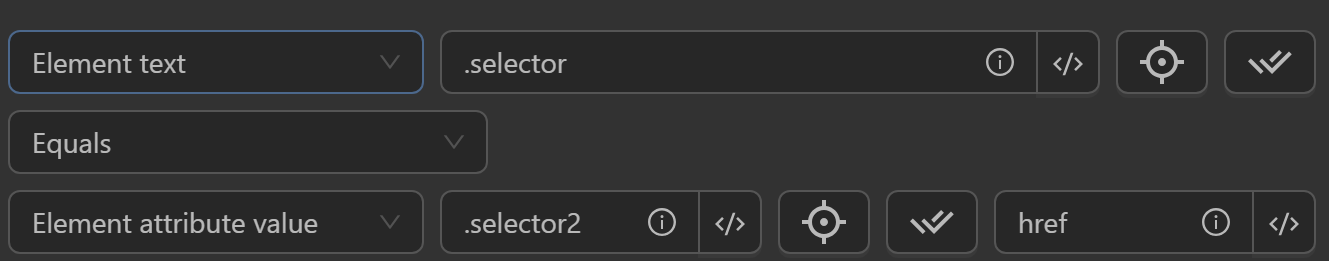
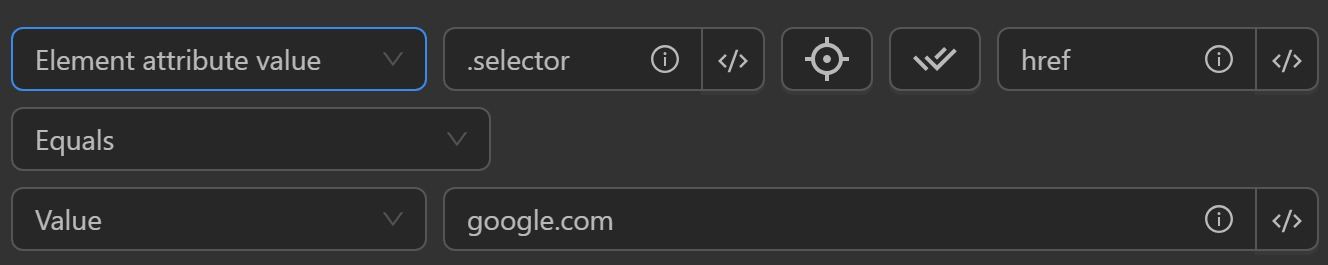
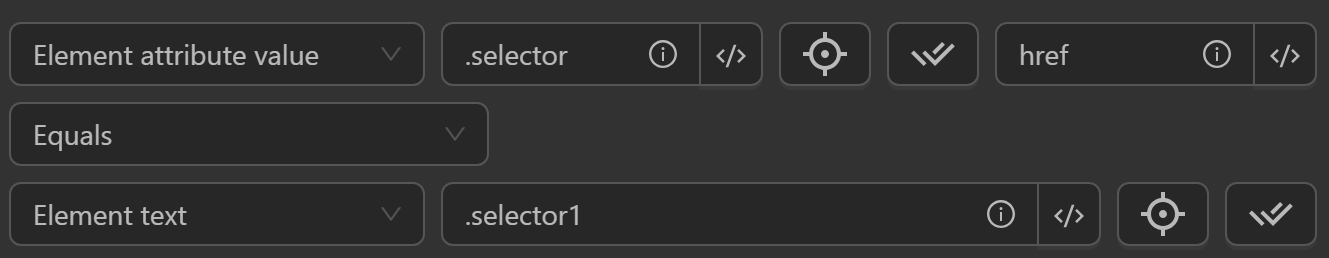
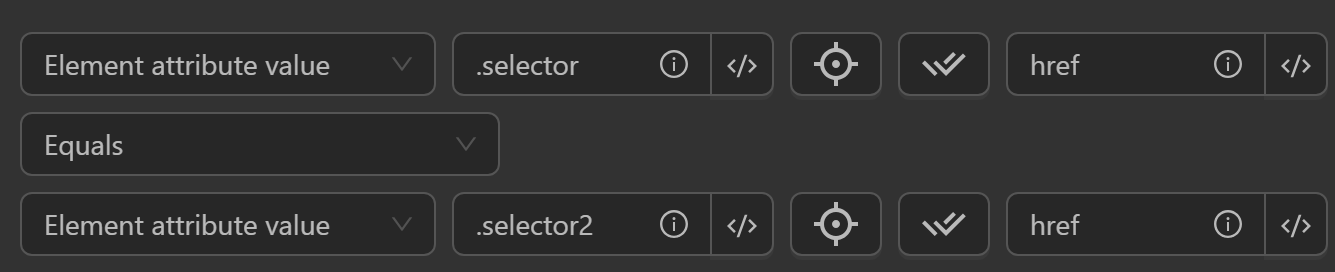
Element Attribute Value
- Compare an element's attribute value with value, element text, or element attribute value.
Comparison Type
Basic
- Equal: Compares if the two sides are
equal, distinguishing between uppercase and lowercase. For example,Anis not equal toan. - Equal (case insensitive): Compares without distinguishing between uppercase and lowercase. For example,
Anis equal toan. - Not Equal: Compares if the two sides are different.
Number
- Greater Than: Compares if the left side is greater than the right side.
- Greater Than or Equal: Compares if the left side is greater than or equal to the right side.
- Less Than: Compares if the left side is less than the right side.
- Less Than or Equal: Compares if the left side is less than or equal to the right side.
Text
- Contains: Checks if the left side (case-sensitive) contains the text on the right side. For example,
google.comis not contained ingoOgle.com/abc. - Contains (case insensitive): Checks if the left side (case-insensitive) contains the text on the right side. For example,
goOgle.comis contained ingoOgle.com/abc. - Not Contains: Checks if the left side (case-sensitive) does not contain the text on the right side. For example,
google.comis not contained ingoOgle.com/abc. - Not Contains (case insensitive): Checks if the left side (case-insensitive) does not contain the text on the right side. For example,
google.comis not contained ingoOgle2.com/abc. - Starts With: Checks if the left side (case-sensitive) starts with the text on the right side. For example,
googleMe.comstarts withgoogle. - Ends With: Checks if the left side (case-sensitive) ends with the text on the right side. For example,
googleMe.comends withcom. - Match with RegEx: Checks if the left side (case-sensitive) matches the RegEx pattern on the right side. For example,
123456matches the RegEx\b[0-9]{6}\b.
Boolean
- Is Truthy: The input value, when converted to a boolean, is
true. For example,abcis a Truthy value. - Is Falsy: The input value, when converted to a boolean, is
false. For example,number::0is a Falsy value.
Note
To distinguish between Truthy and Falsy values, refer to this resource.
