Expressions
Below are the expressions you can use in OmniLogin's Automation
Global Data
Global Data is data that can be used in your workflow. You can add data from a file into the global data
Example
First, you will input values into Global Data
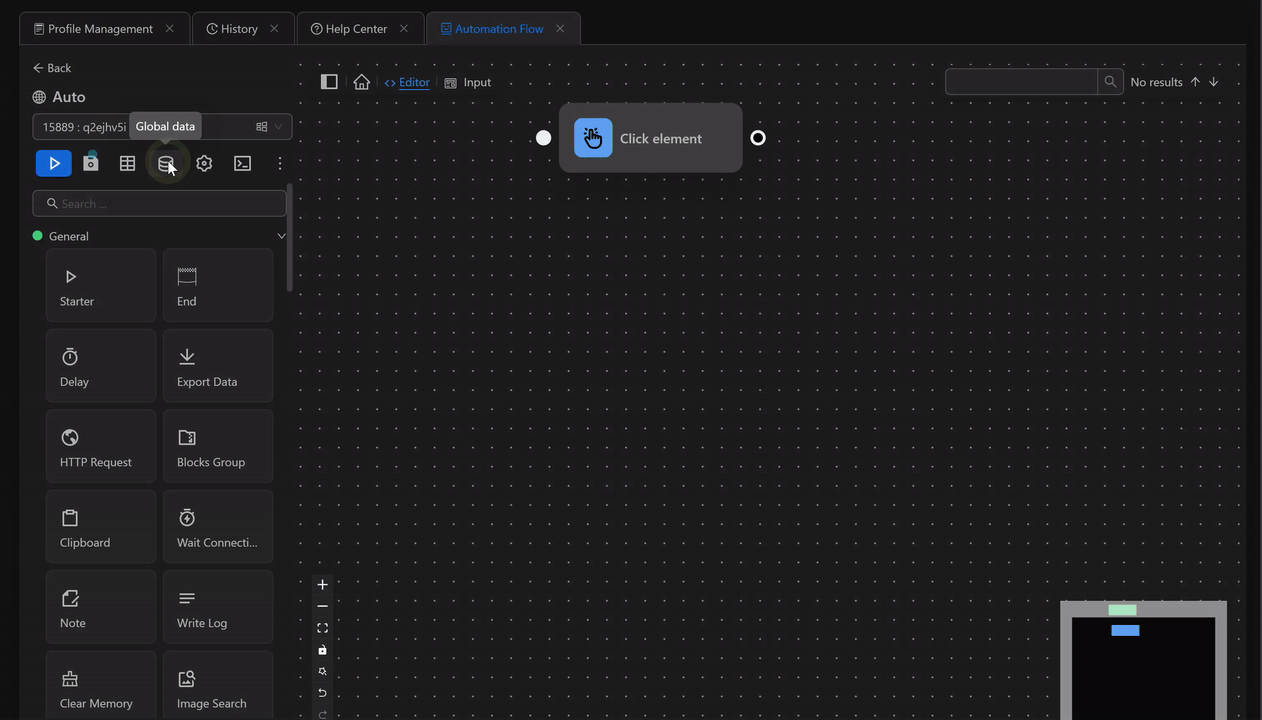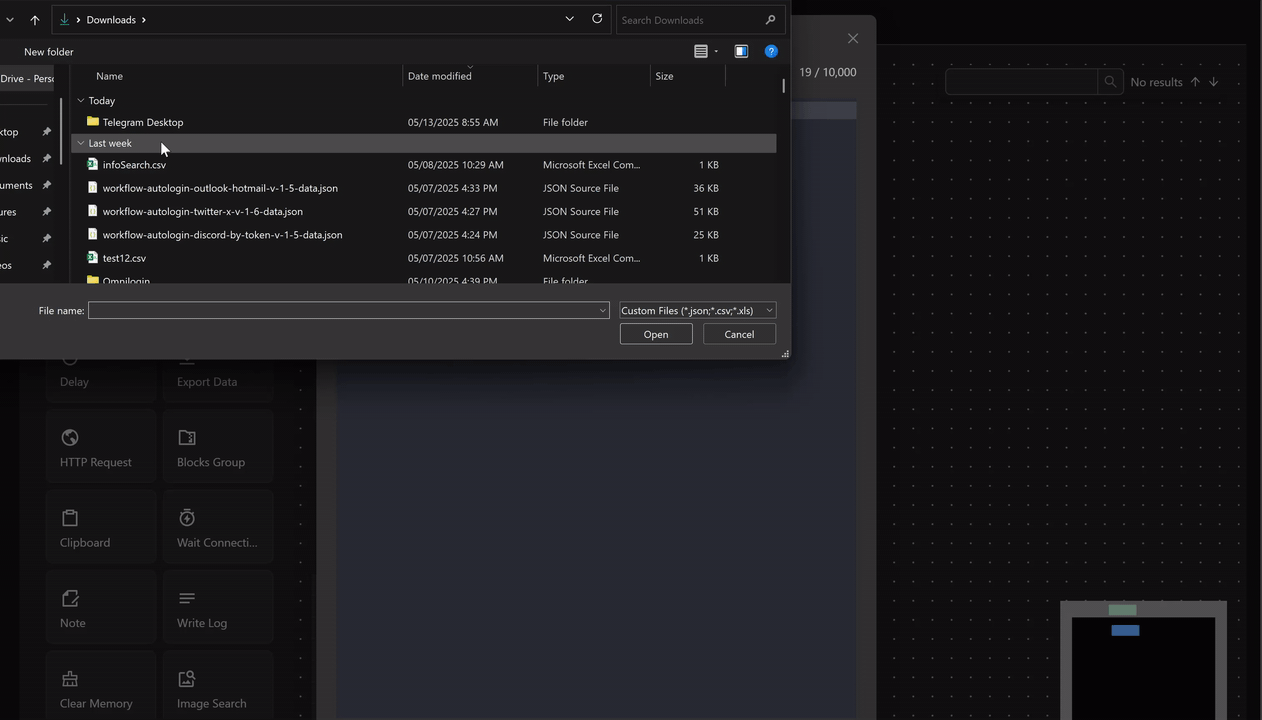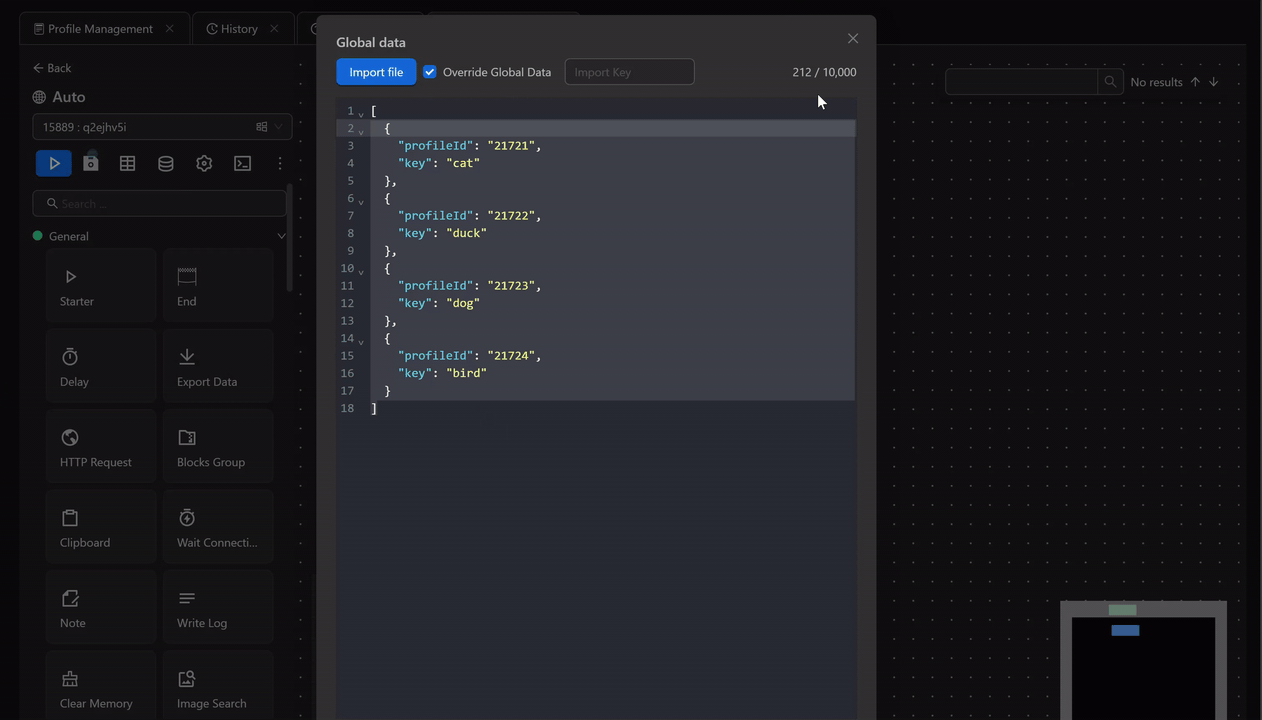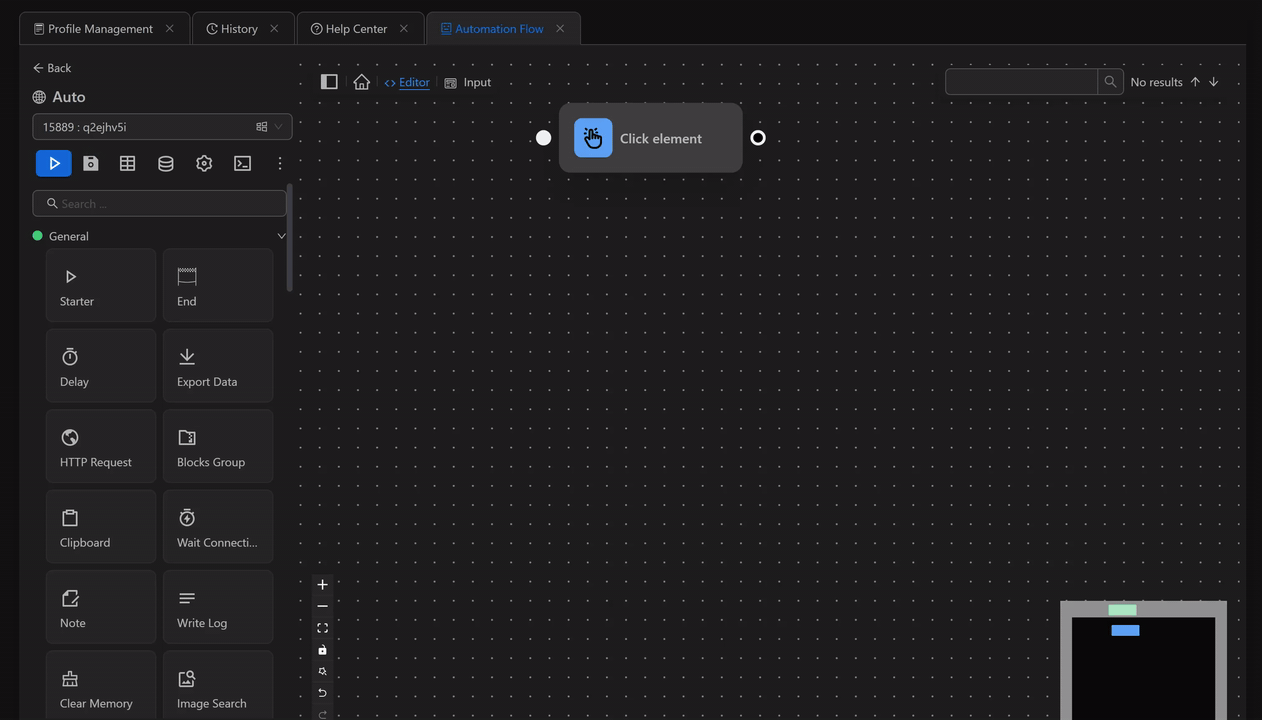
Then open Google using the Open URL node and use the expression {{globalData.0.key}} to retrieve the first value of the key field in the Press Key node.
Previous Block
Each time a block is executed
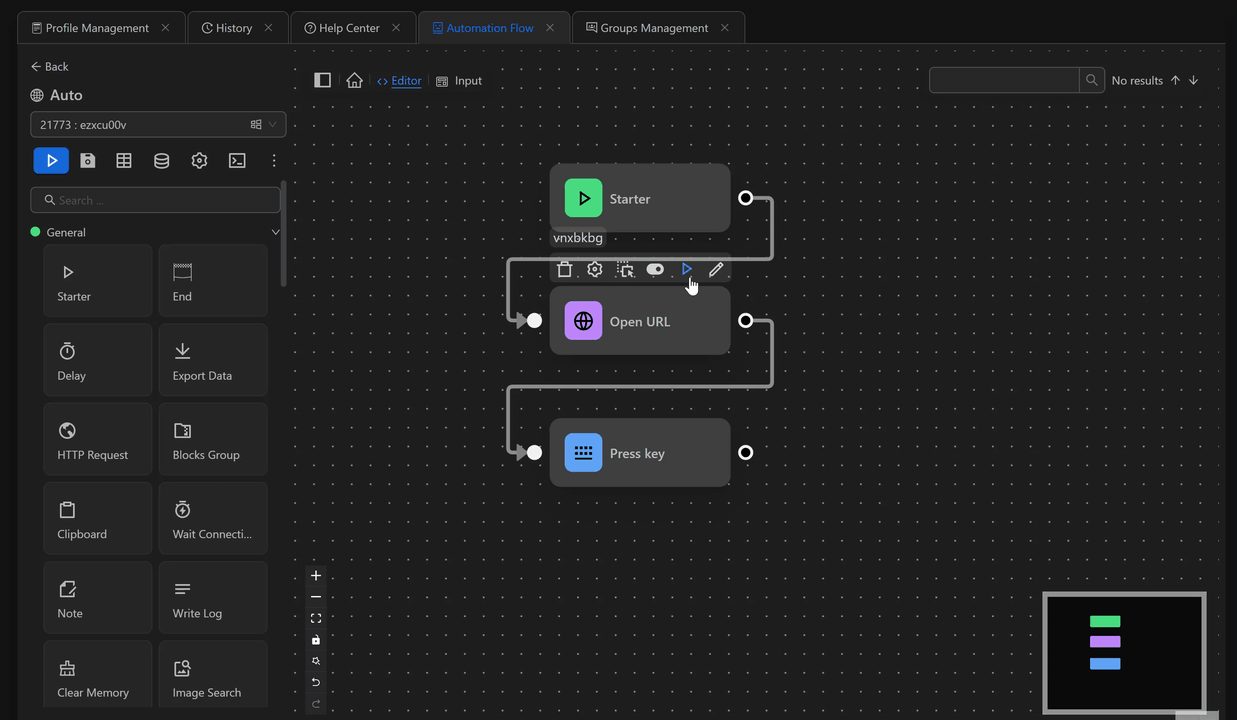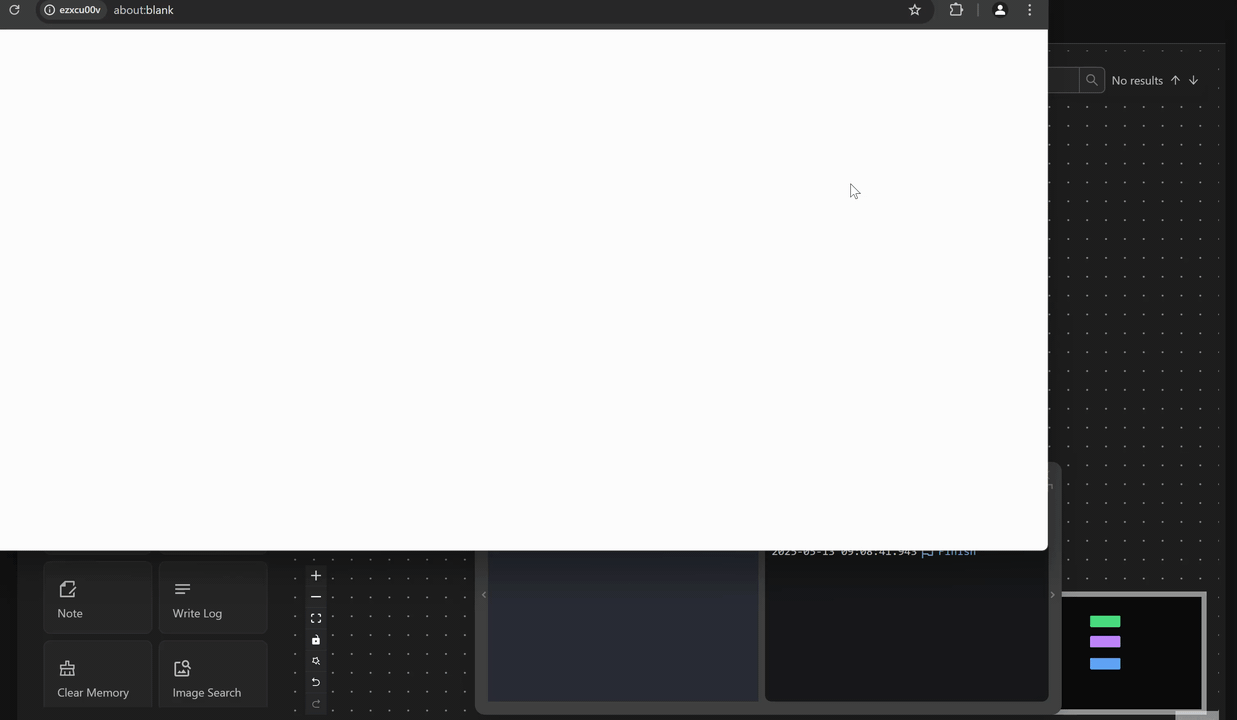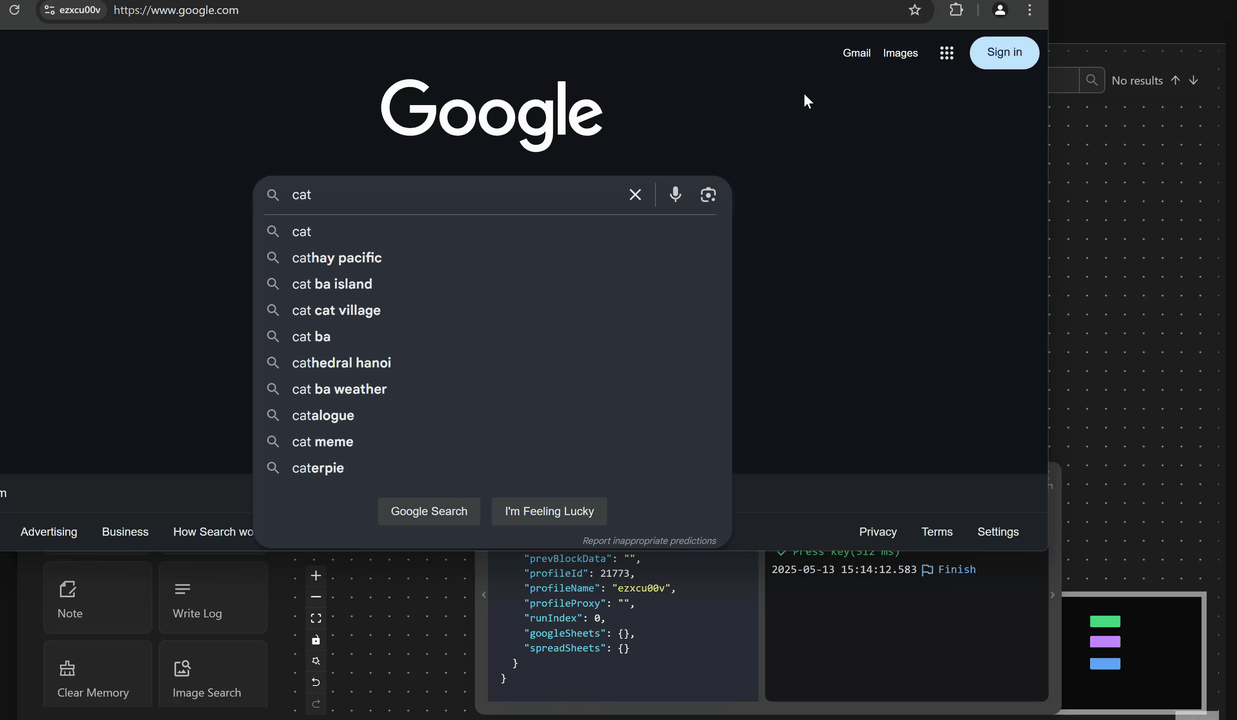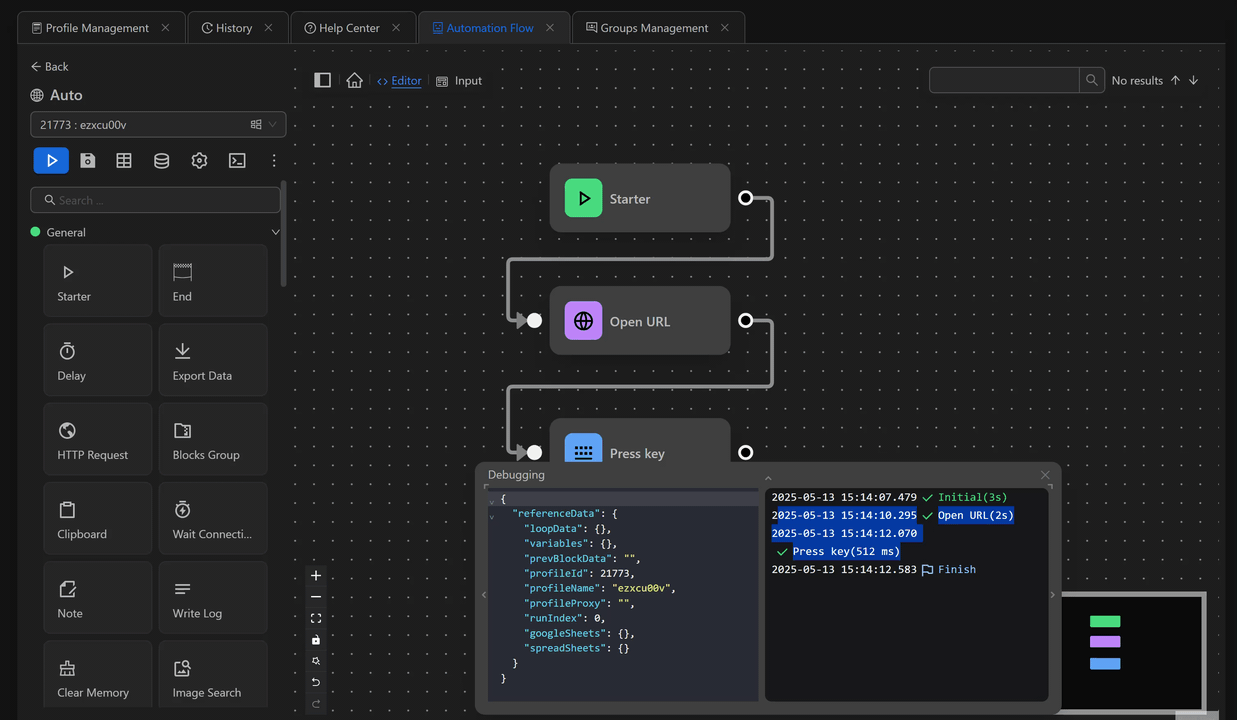
Example of outputting the value of the previous node using the Press Key node
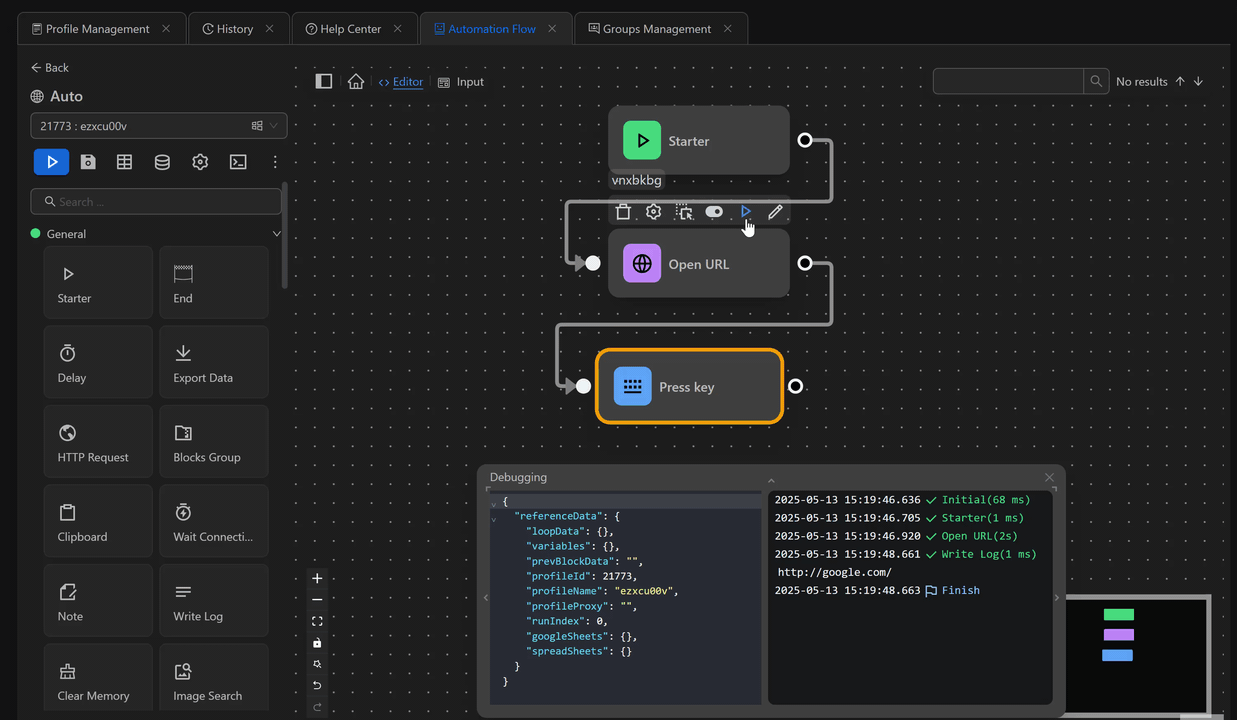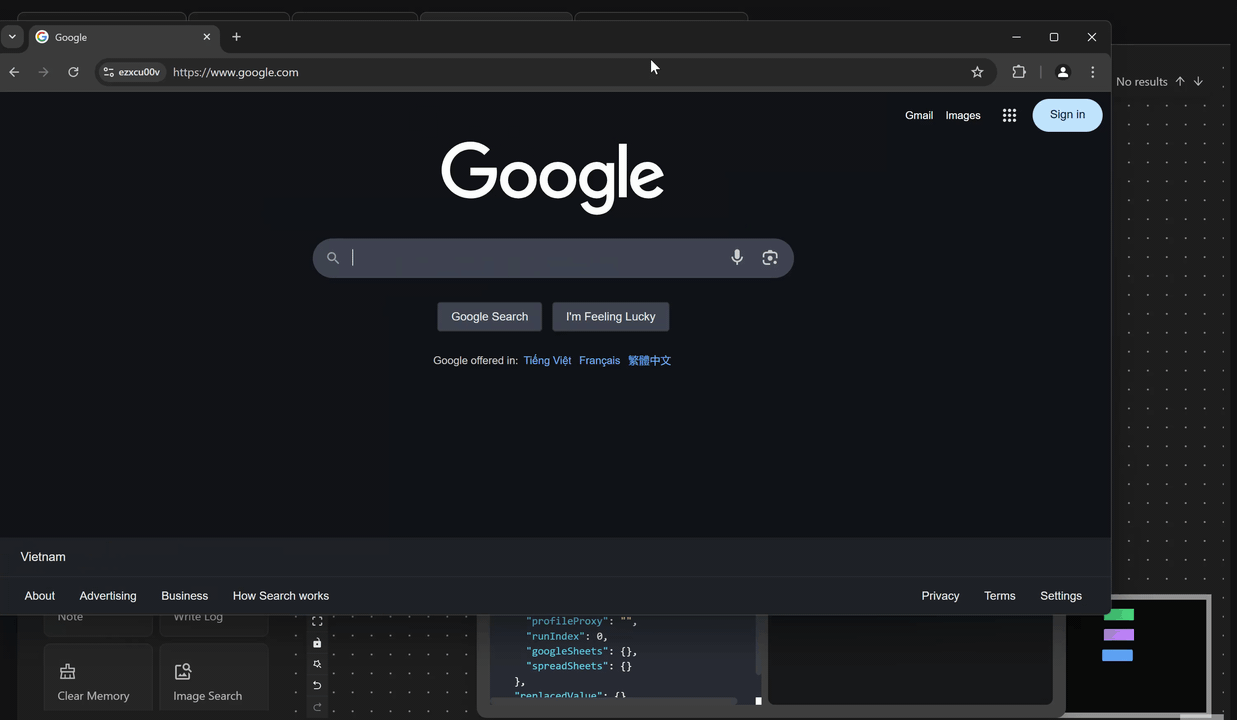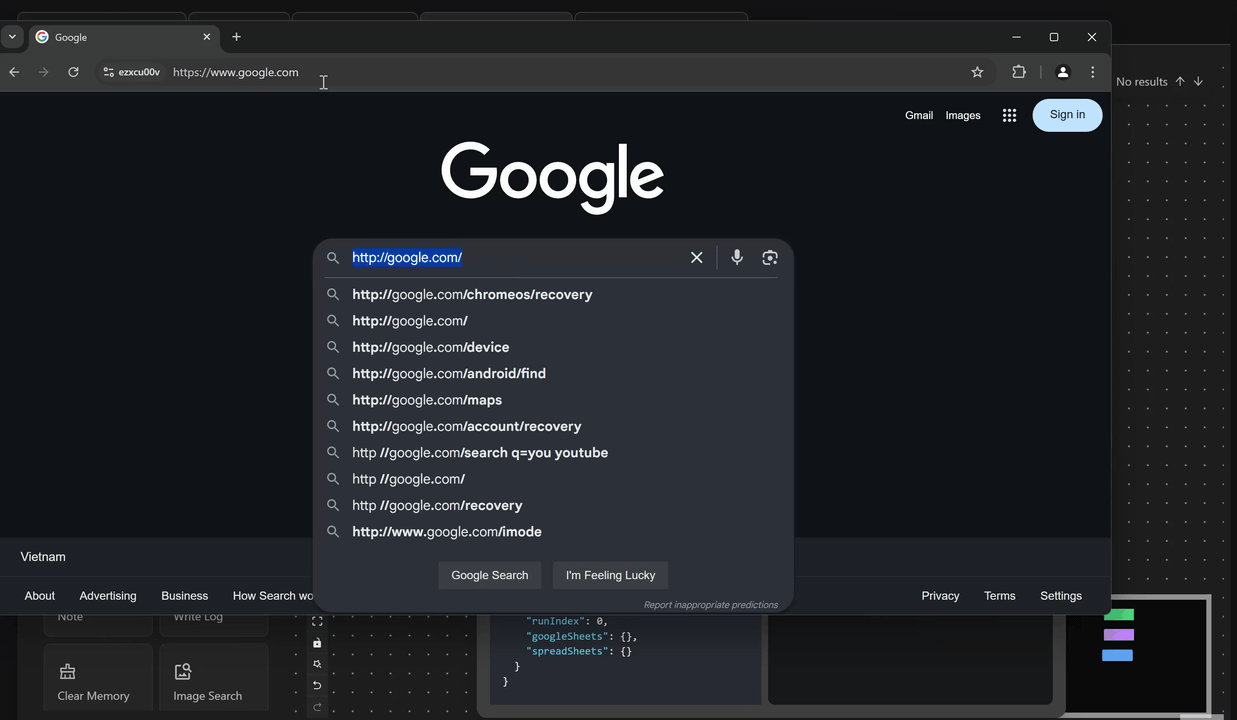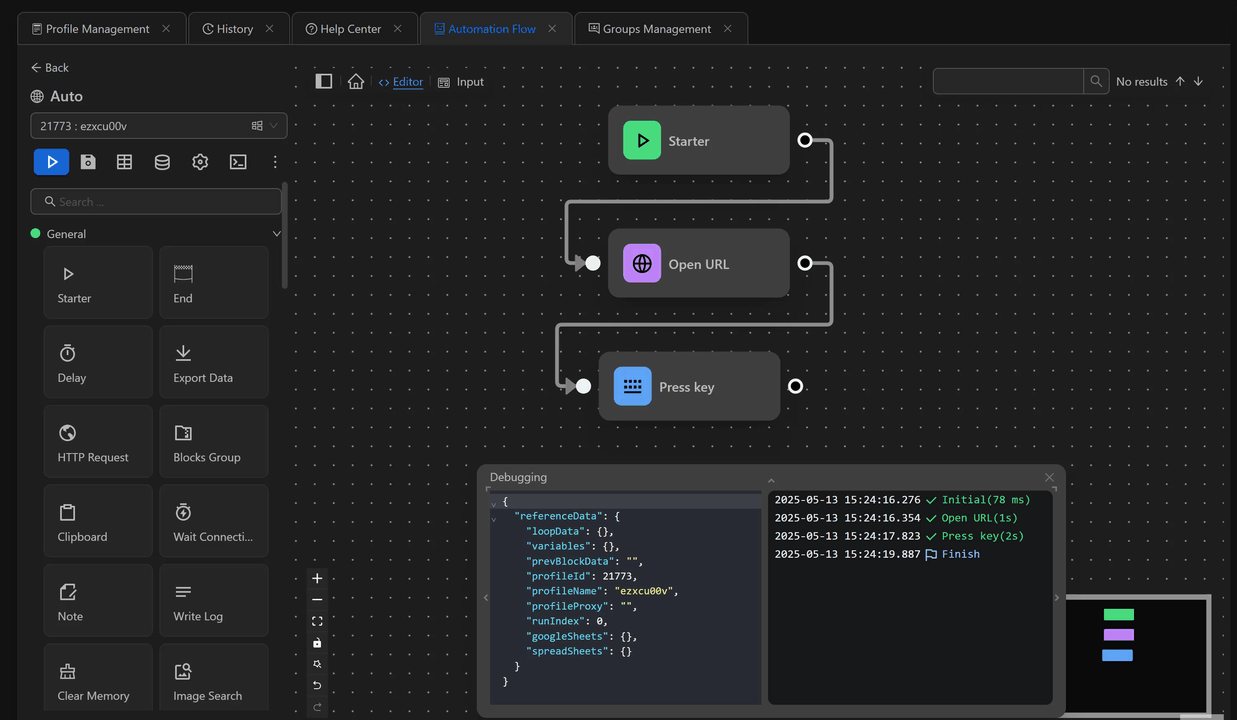
First, you will open the google.com page using the Open URL node. Next, retrieve the value of the previous node and output it to the search bar of the page using the expression {{prevBlockData}} with the Press Key node right after the Open URL node. The value printed is the URL of the page you just opened.
Accessing Other Data Within an Expression
To access other data within an expression, you must wrap the expression for accessing data in brackets ([]). For example, you cannot use the expression {{globalData.{{variables.a}}}} but must write {{globalData.[variables.a]}}
Functions
All built-in functions always start with the prefix $; for example: $funcName(param). Here is a reference list of the functions available in Automation.
$date(date, dateFormat?)
Retrieves or formats a date. This function has two parameters, with the second one being optional.
If you want to format the current date, you can directly pass dateFormat as the first parameter, for example, {{ $date('dd-MMMM-yyyy') }}, and the result will be 14-September-2023. See all available date formats on this page.
For the date parameter, see valid date formats on the MDN page.
Example
You can use the date function in various ways as follows
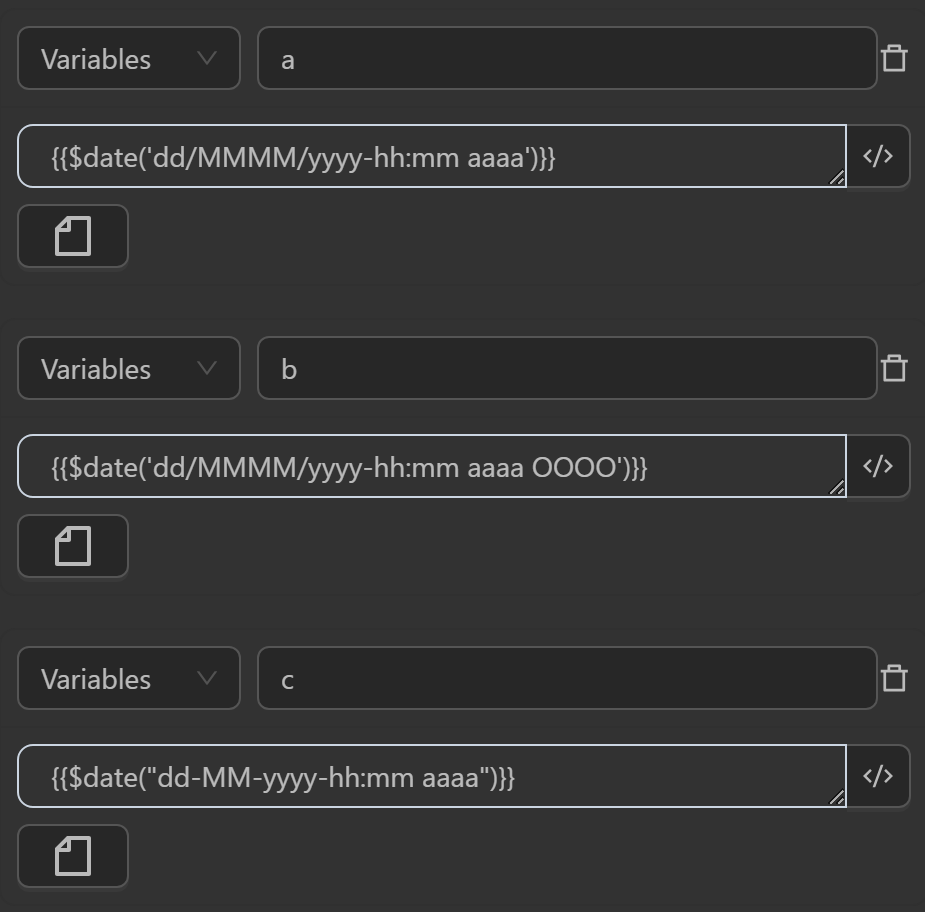
With the above expression you will display the following values
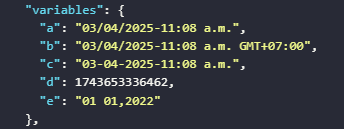
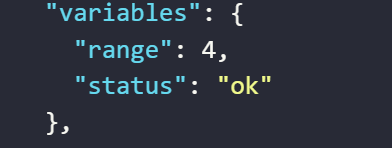
The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression generates the current date with the formatday/month/year/hour:minute AM/PMThe value assigned to the variable
bby the expression generates the current date with the formatday/month/year/hour:minute AM/PM timezoneThe value assigned to the variable
cby the expression generates the current date with the formatday-month-year-hour:minute AM/PMThe value assigned to the variable
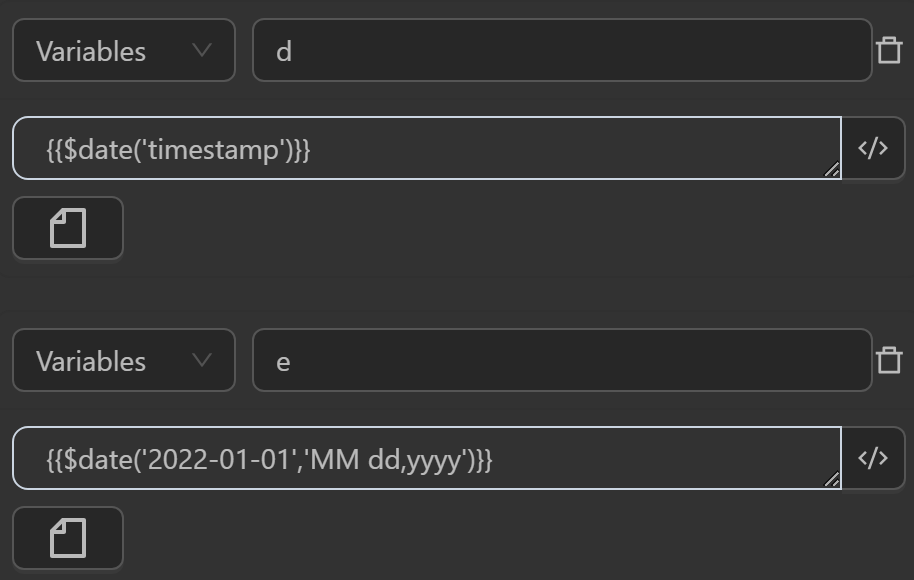
dby the expression generates the current date with the format timestamp at the current momentThe value assigned to the variable
eby the expression returns the desired format with the input time parameter
$rand(min?, max?)
The $rand function generates a random number in the range from min to max (inclusive). If both min and max are integers, it returns a random integer in the range. If either min or max is not an integer, it returns a random decimal number in the range.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
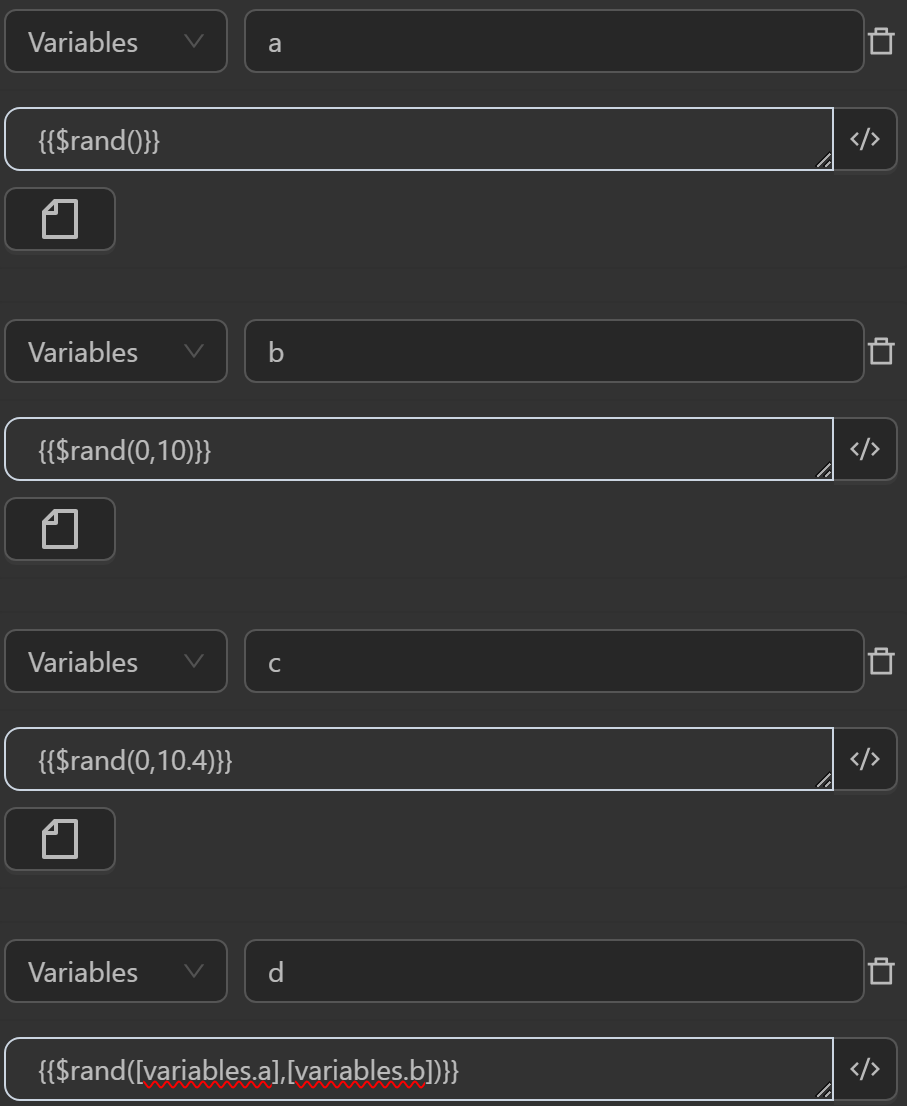
When running you will see the variables receiving the following values
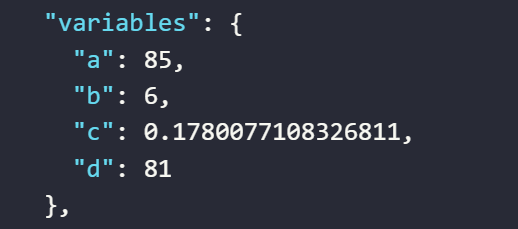
The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression randomly generates a number in the range from0to100The value assigned to the variable
bby the expression randomly generates a number in the range from0to10The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression randomly generates a number in the range from0to10.4, which will always produce a decimal digitThe value assigned to the variable
dby the expression randomly generates a number in the range of the values of variablesatob
$randint(min?, max?)
This randint function generates a random integer in the range from min to max (inclusive). If min and max are not provided, it defaults to the range from 0 to 100.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
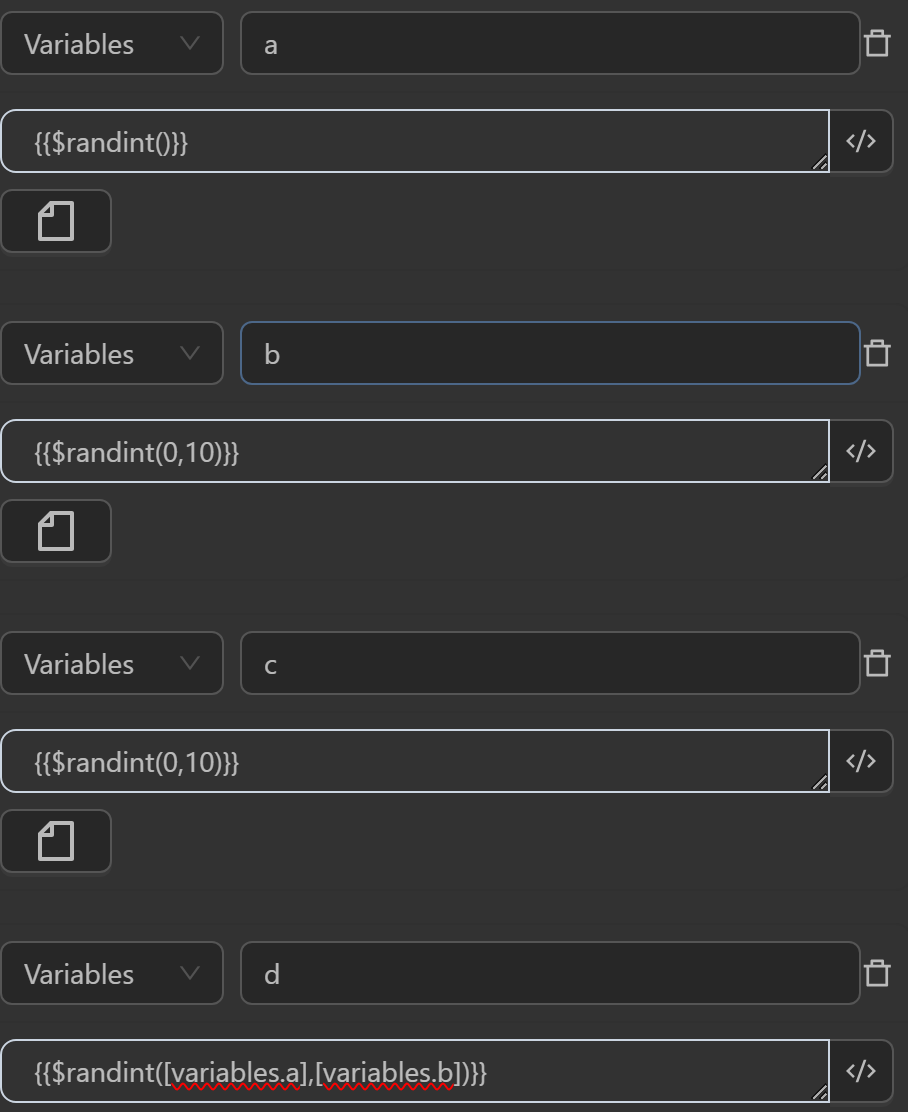
When running you will see the variables receiving the following values
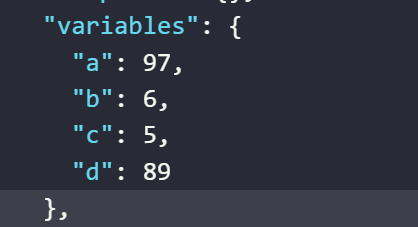
The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression randomly generates a number in the range from0to100The value assigned to the variable
bby the expression randomly generates a number in the range from0to10The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression randomly generates a number in the range from0to10.4. Since it is a function that generates random integers, the result will be a positive integerThe value assigned to the variable
dby the expression randomly generates a number in the range of the values of variablesatob
$getLength(str)
This function attempts to parse the input string str into JSON. If successful, it returns the length of the resulting value. If parsing fails (i.e., str is not valid JSON), it returns the original string str.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
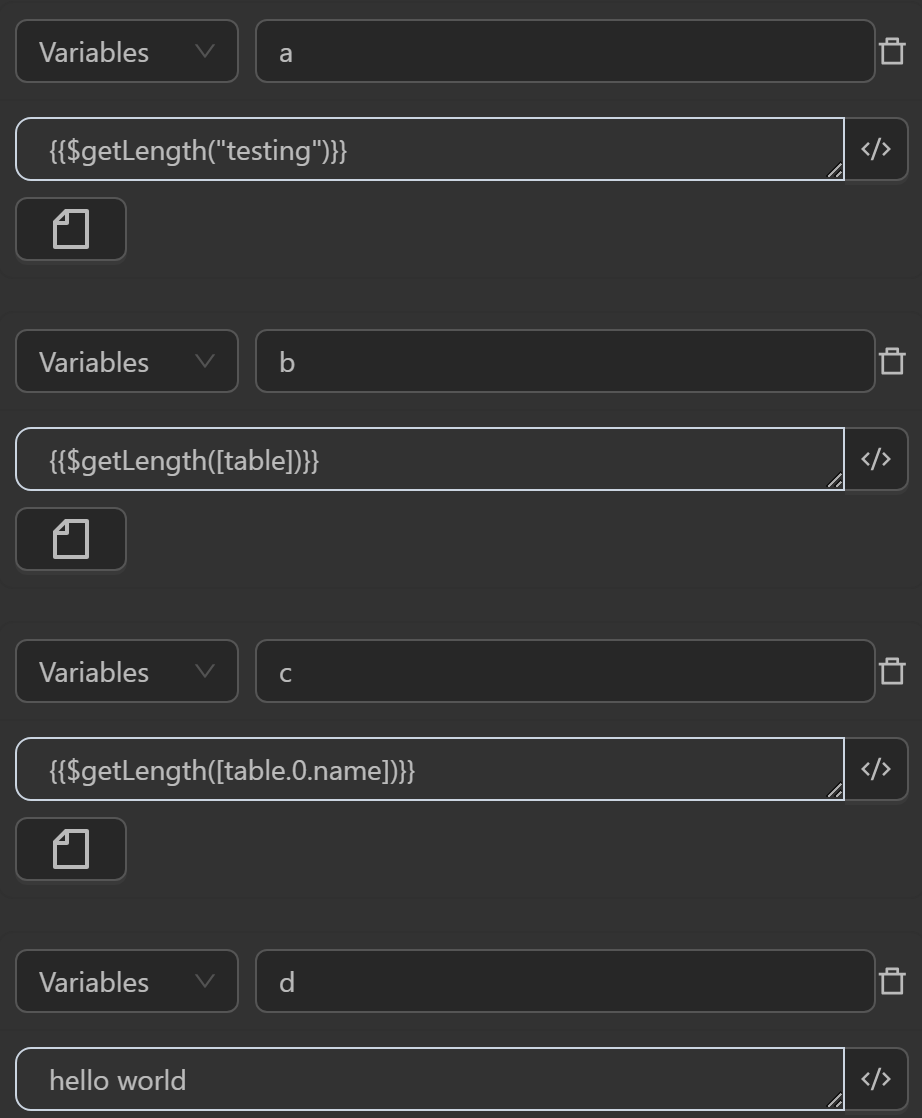
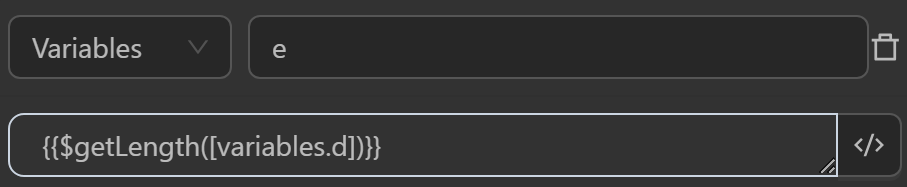
When running you will see the variables receiving the following values
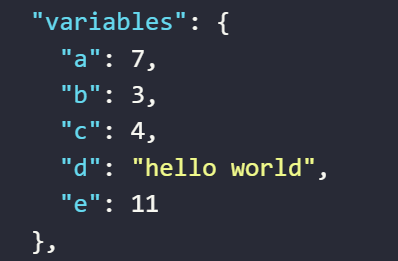
The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression calculates the length of a text stringThe value assigned to the variable
bby the expression calculates the length of a table
The length of the table is the number of elements in an array. As shown in the image you have an array with 3 object elements, so the length result will be 3
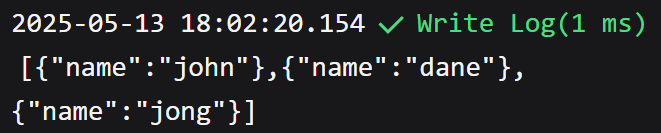
- The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression calculates the length of the first data in the table
As shown in the image, the first element in the table is the object {"name":"john"}, and the value in the name column is john. The length of that string will result in 4 !
- The value assigned to the variable
eby the expression calculates the length of a variable containing a text string
$getOTP(secret)
This function takes a parameter as a string and then generates an OTP code based on that string. Typically, this function is used when you want to retrieve the 2FA code entered.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
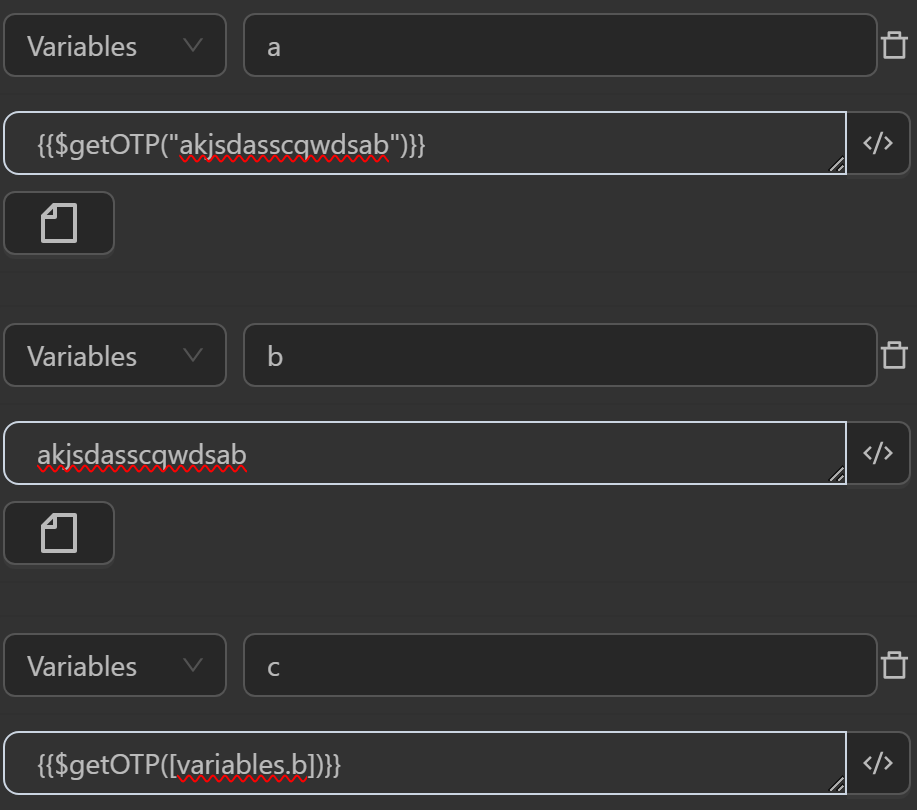
The result returned will be as follows
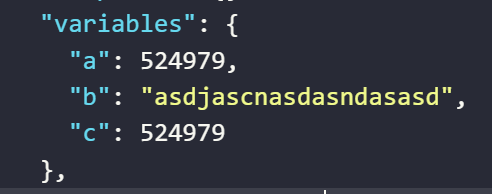
The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression generates an OTP code based on an input stringThe value assigned to the variable
cby the expression generates an OTP code based on an input variableb
Note
You need to set the time on the machine to match the actual time to avoid errors with this function
$randData(text)
This randData function generates a random character or string based on the input text. If text is a string, it replaces any occurrence of a question mark (?) followed by a letter with a random character of the corresponding type (lowercase, uppercase, digit, special character, or a combination of these).
?l: lowercase letter?u: uppercase letter?d: digit?f: lowercase + uppercase?s: symbol?m: uppercase + digit?n: lowercase + digit?a: any
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
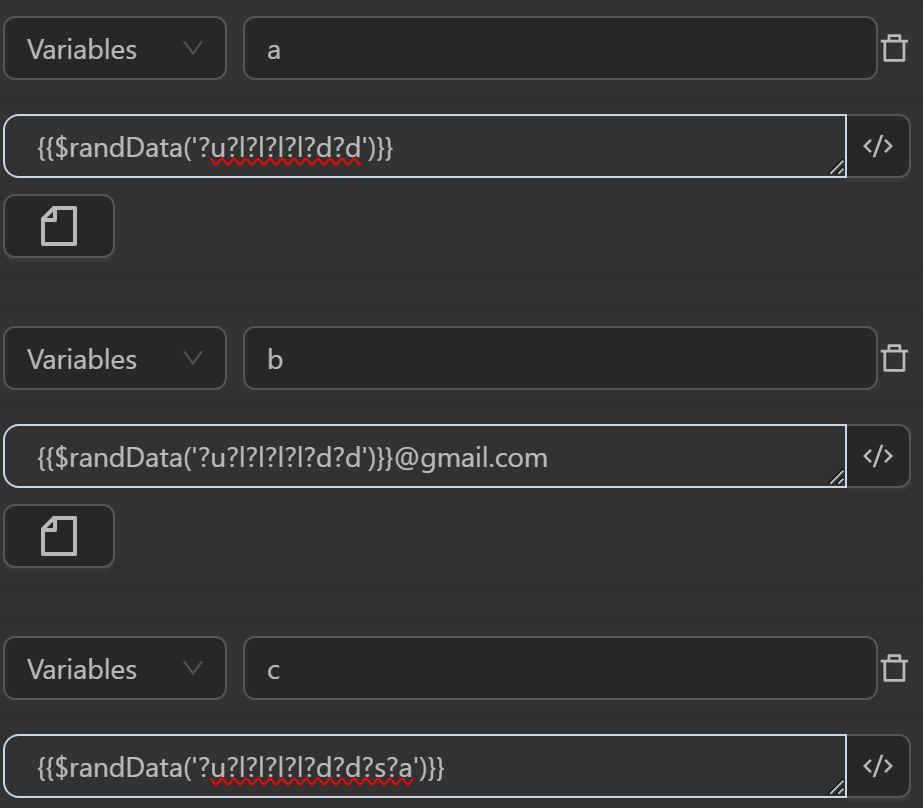
The result returned will be as follows
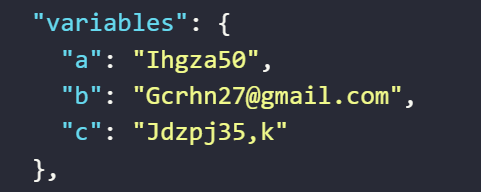
The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression generates a string consisting only ofuppercase letters, lowercase letters, and digitsThe value assigned to the variable
bby the expression generates a string consisting only oflowercase letters and digits, then appends @gmail.com to randomly generate a Gmail addressThe value assigned to the variable
cby the expression generates a string consisting only oflowercase letters, digits, symbols, and any
$randDate(minDate?, maxDate?, dateFormat?)
The function generates a random timestamp within the range of two parameters minDate (starting from 01-01-1990) and maxDate in any display format of dateFormat. The default format is dd-MM-yyyy: 12-12-2000. If you want to change the format, you can add dateFormat after the time range.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
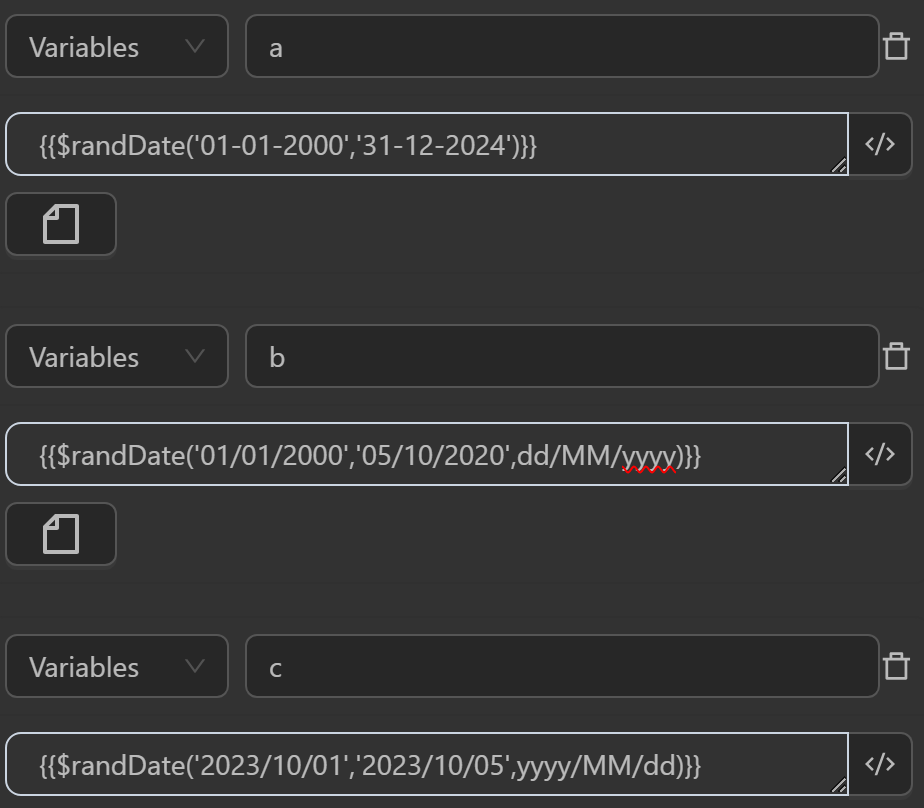
The result returned will be as follows
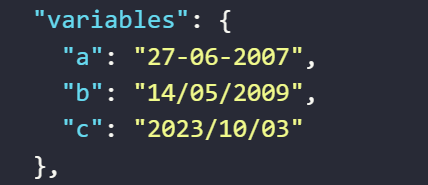
The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression randomly generates a time unit in the default formatday-month-yearThe value assigned to the variable
bby the expression randomly generates a time unit in the formatday/month/yearThe value assigned to the variable
cby the expression randomly generates a time unit in the formatyear/month/day
$randPick(data)
The function randomly selects one element from the data array data. This function is commonly used when you input an array into the function.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
First, create an array with 3 elements
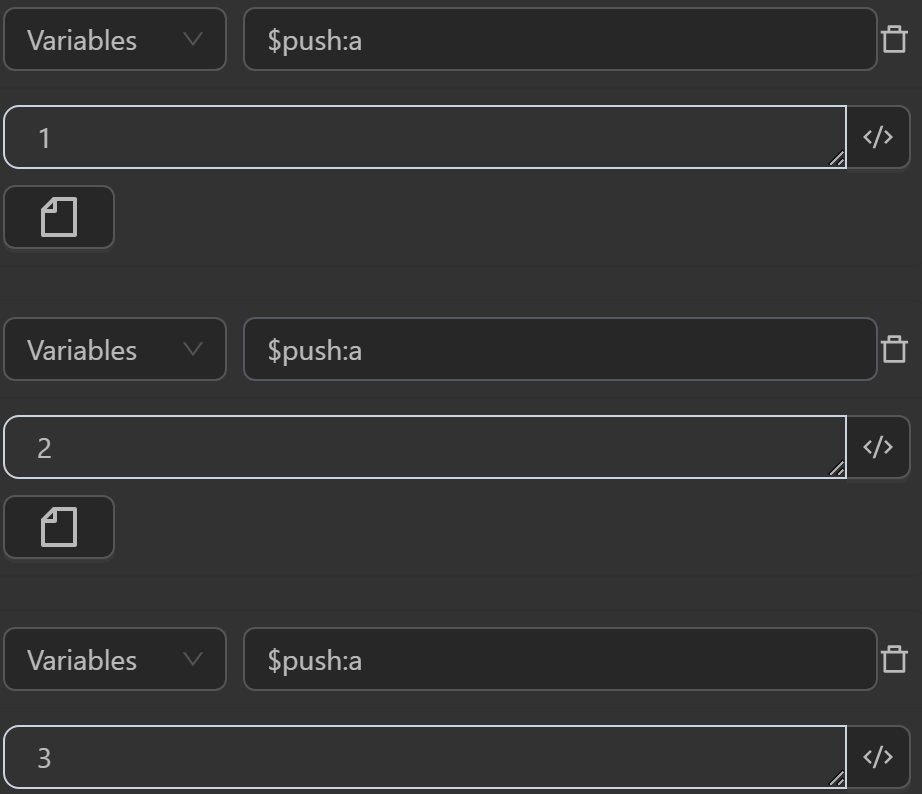
Then use the expression {{$randPick([variables.a])}} in the Write Log node to return a random element from the a array
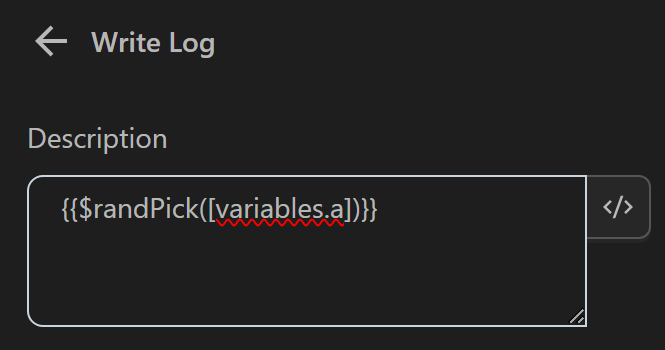
The result returned will be as follows
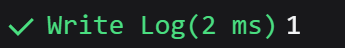
$randChoice(...data)
This function is quite similar to the randPick function, as both select a random element from an array. However, this function allow you to directly add elements to the function for use. When values are added, it automatically converts them into an array and performs the action of selecting one random element. You typically use this function when you want to randomly select a value from a list within the function.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
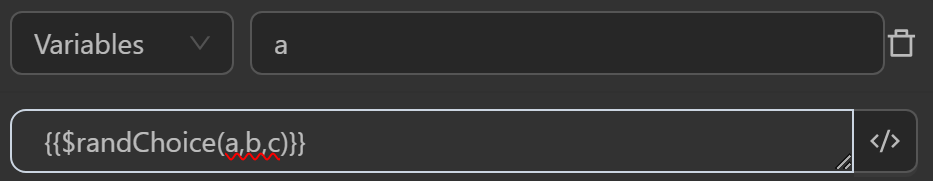
The result returned will be as follows
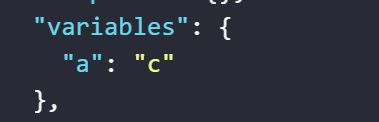
The value assigned to the variable a by the expression randomly selects an element from the input list of elements
$split(value, param)
This split function splits a string into an array of substrings based on a specified delimiter param. If no delimiter is provided, it defaults to a space. If the input value is not a string or is empty, the function returns the original value.
Common case example
Typically you will use this function as follows 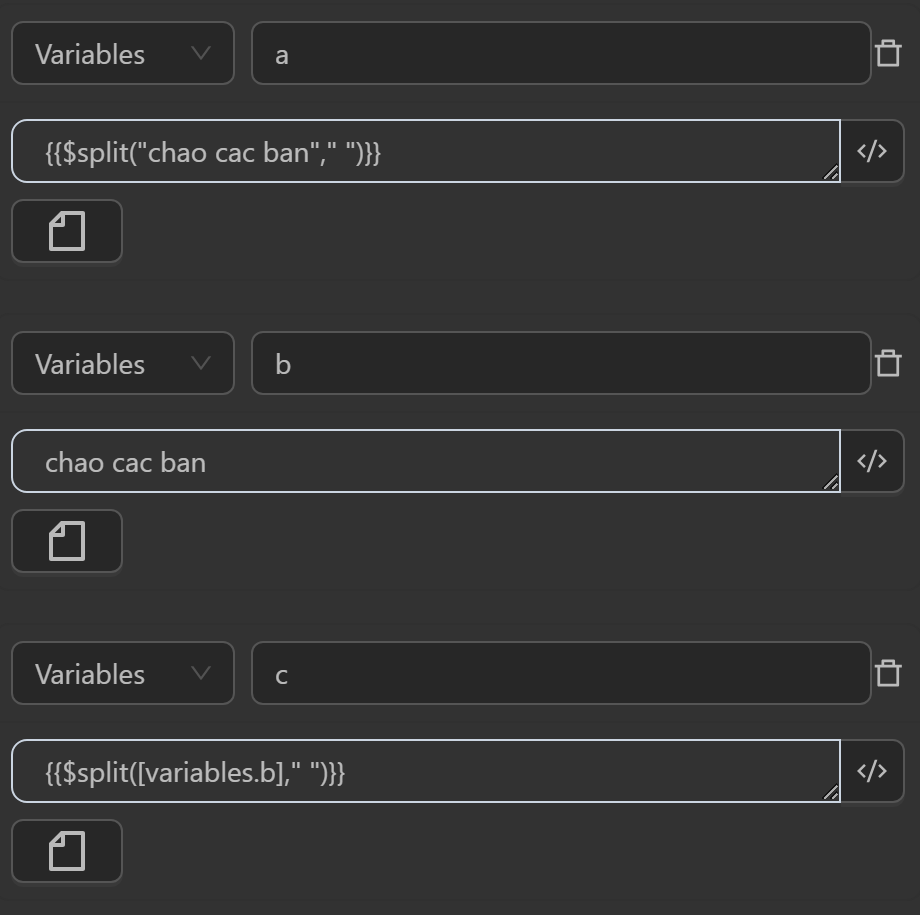
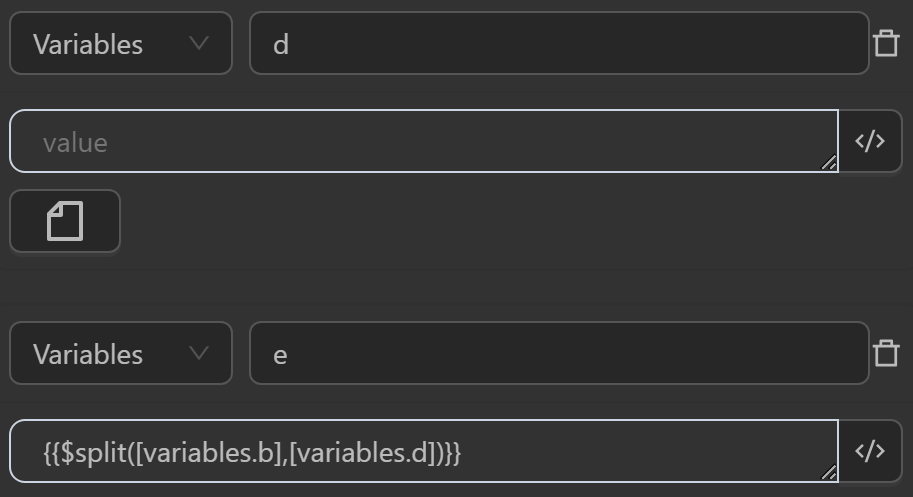
The value after running will display as follows
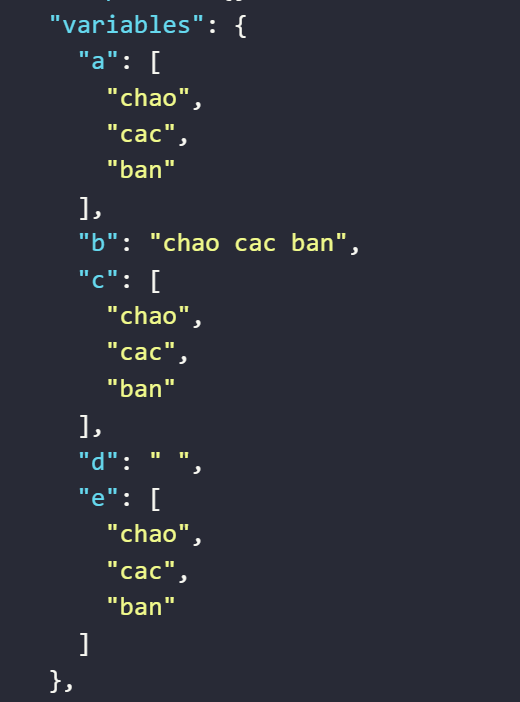
The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression converts the input string based on the delimiter" "The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression converts a variable with a string value based on the delimiter" "The value assigned to the variable
eby the expression converts a variable with a string value based on the delimiter" "assigned to the variabled
Example of splitting a string separated by line breaks
In the case where the input values are separated by line breaks 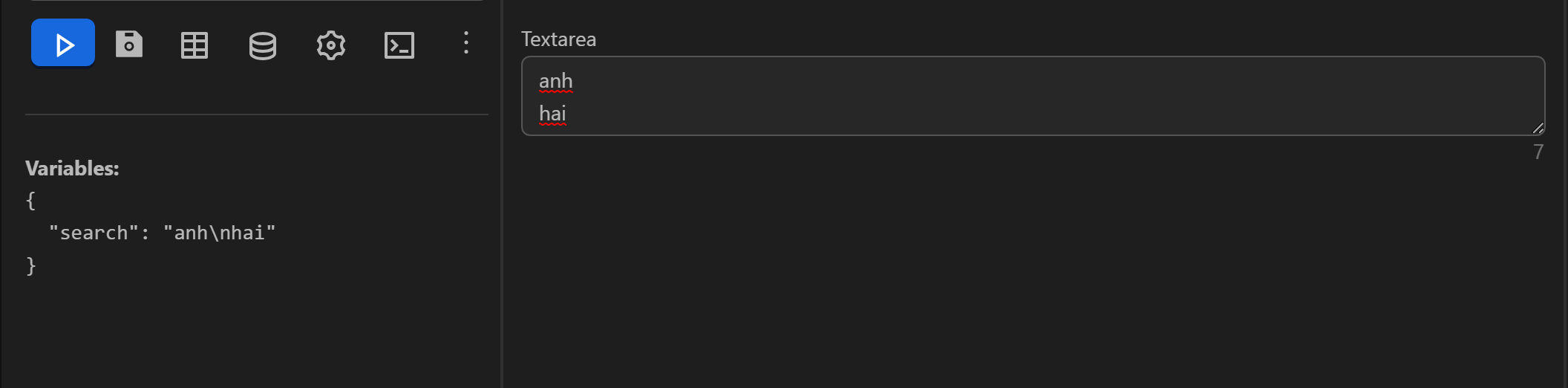
In this case, you cannot use the expression as in the examples above. You need to create a variable and insert the line break value by pressing Enter in the variable’s value input field. Then use the split expression with the param value as the expression retrieving the delimiter variable value, which is variables.delimiter. The expression to split the string into an array will be as follows
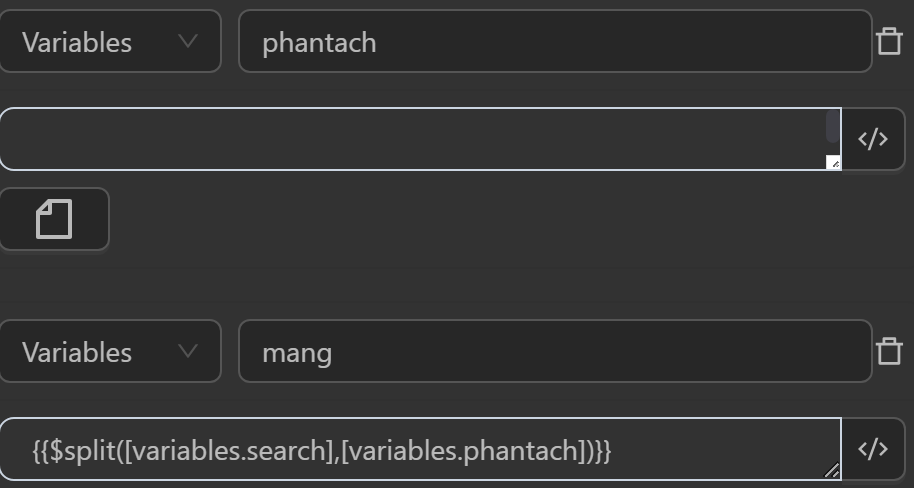
The returned value will be an array containing the input values

$increment(value, incrementBy)
This function increases a value by adding value and incrementBy. If either is not a number, the original value is returned.
Example
You will use this function in the following cases 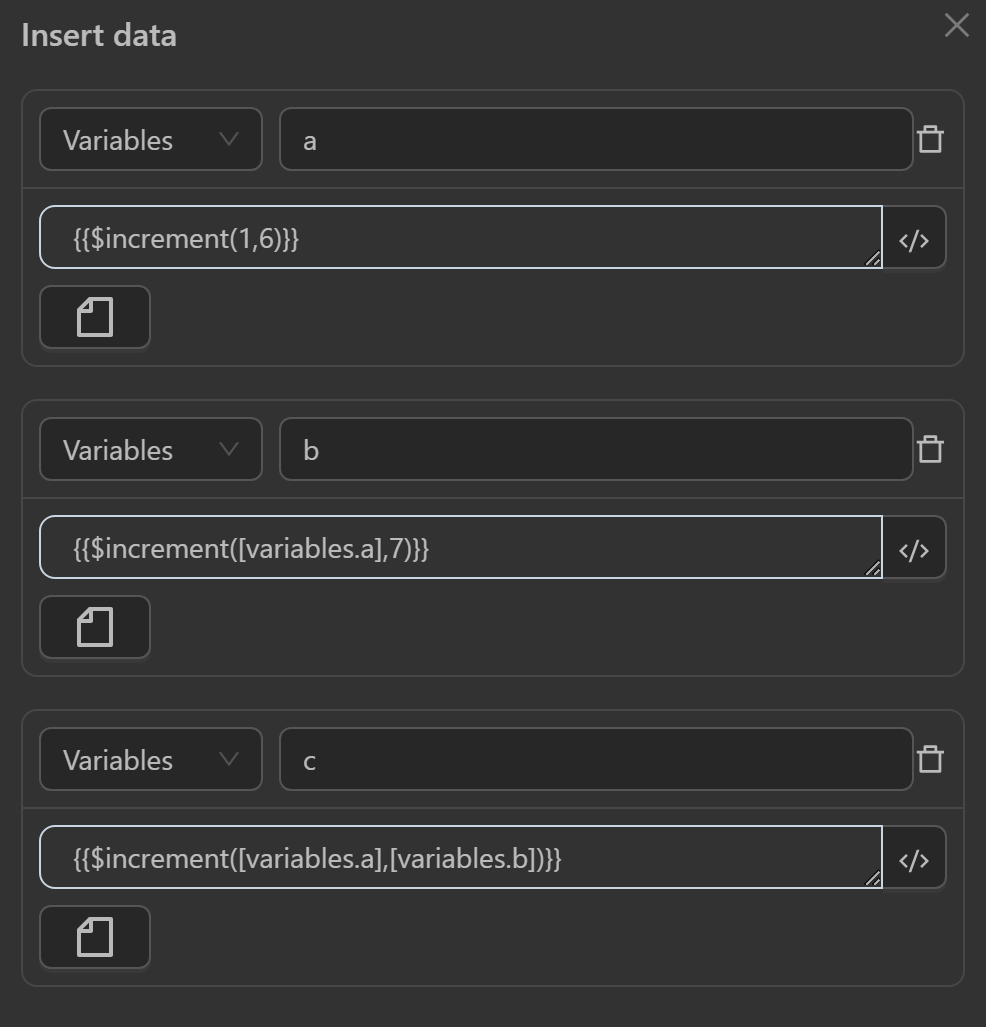
The returned value will be as follows
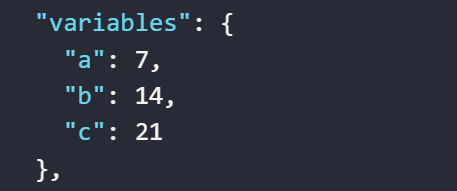
- The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression adds two numbers - The value assigned to the variable
bby the expression adds a variable’s value to a number or vice versa - The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression adds the values of two variables together
$subtract(value, incrementBy)
This function subtracts incrementBy from value if both are numbers; otherwise, it returns the original value of value.
Example
You will use this function in the following cases 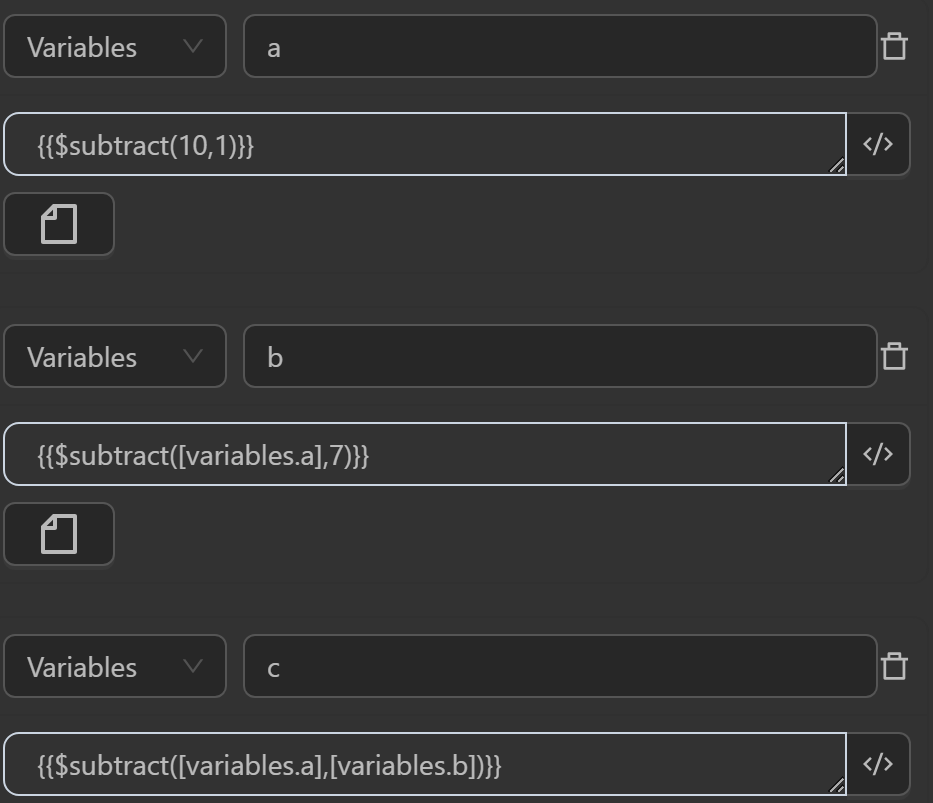
The returned values will be as follows

The value assigned to variable
ais from an expression subtracting two numbersThe value assigned to variable
bis from an expression subtracting a variable’s value from a number or vice versaThe value assigned to variable
cis from an expression subtracting the values of two variables from each other
$increment(value, incrementBy)
This function increases the value by adding a certain amount, but only if both the value and the increment are numbers. If either is not a number, the original value is returned.
Example
You will use this function in the following cases 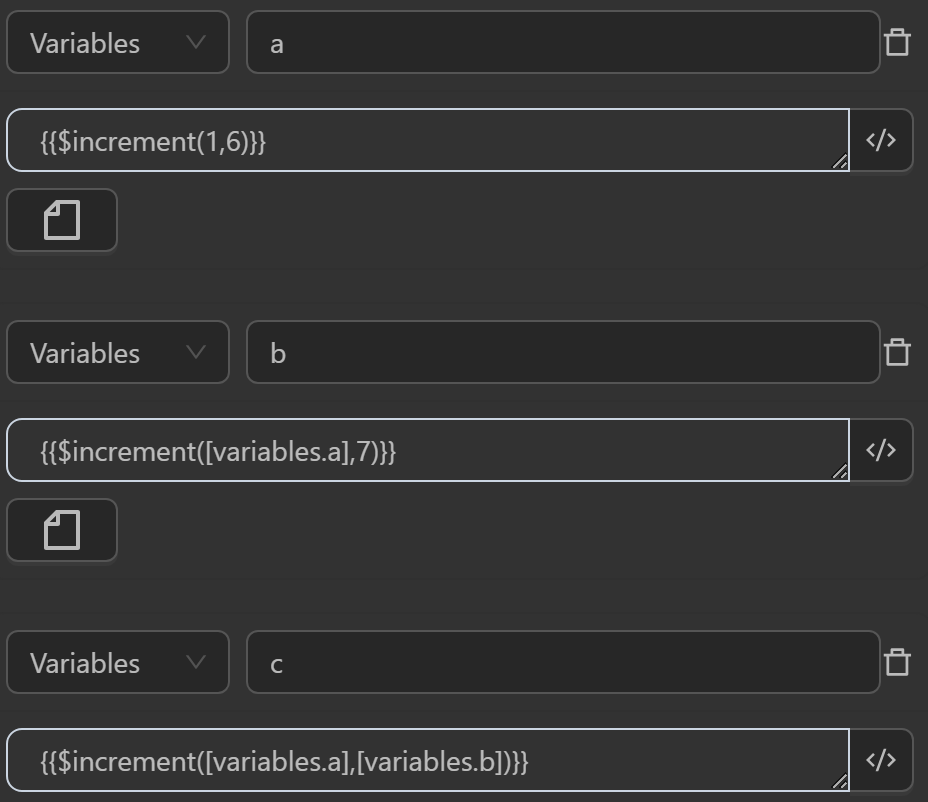
The returned value will be as follows

- The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression adds two numbers - The value assigned to the variable
bby the expression adds a variable’s value to a number or vice versa - The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression adds the values of two variables together
$subtract(value, incrementBy)
This function subtracts subtractBy from value if both are numbers; otherwise, it returns the original value of value.
Example
You will use this function in the following cases 
The returned value will be as follows

- The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression subtracts two numbers - The value assigned to the variable
bby the expression subtracts a variable’s value from a number or vice versa - The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression subtracts the values of two variables from each other
$multiply(value, multiplyBy)
This function multiplies two values together, but only if both values are numbers. If either value is not a number, it returns the original value.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
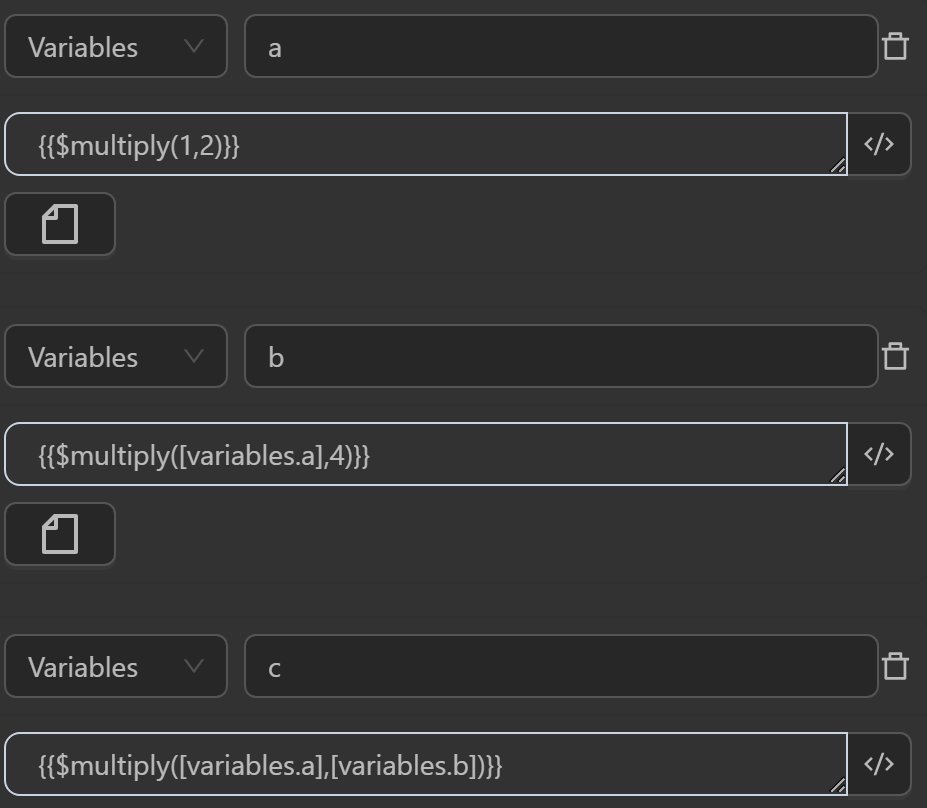
The result returned will be as follows
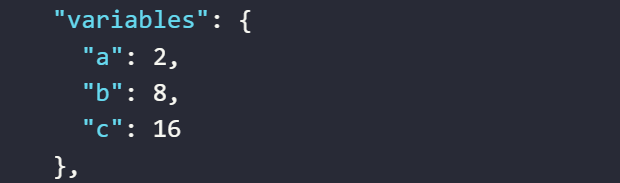
- The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression multiplies two numbers together - The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression multiplies a variable’s value by a number - The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression multiplies the values of two variables together
$divide(value, incrementBy)
This function divides value by divideBy and returns the result. However, if value or divideBy is not a number, it returns the original value instead of performing the division.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
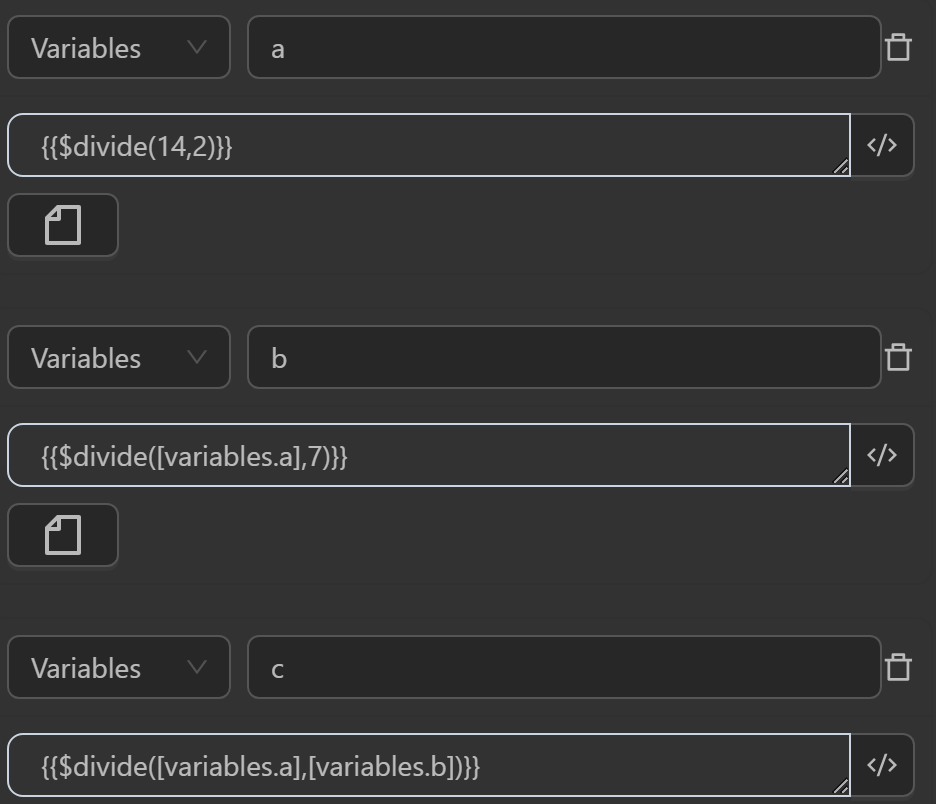
The result returned will be as follows
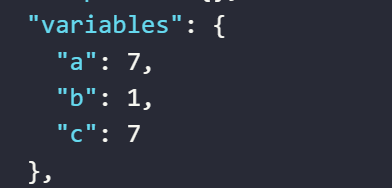
- The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression divides two numbers - The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression divides a variable’s value by a number - The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression divides the values of two variables
$slice(value, start, end)
The slice function extracts a portion of a string or array value and returns a string from start to end. The last element of the new string will be before the end position. For example, if you want to extract a string where the 5th element is a and the 6th is b up to the 6th element, it will only take the value a. Additionally, if only start is provided without end, the extracted string will run from start to the end of the string.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
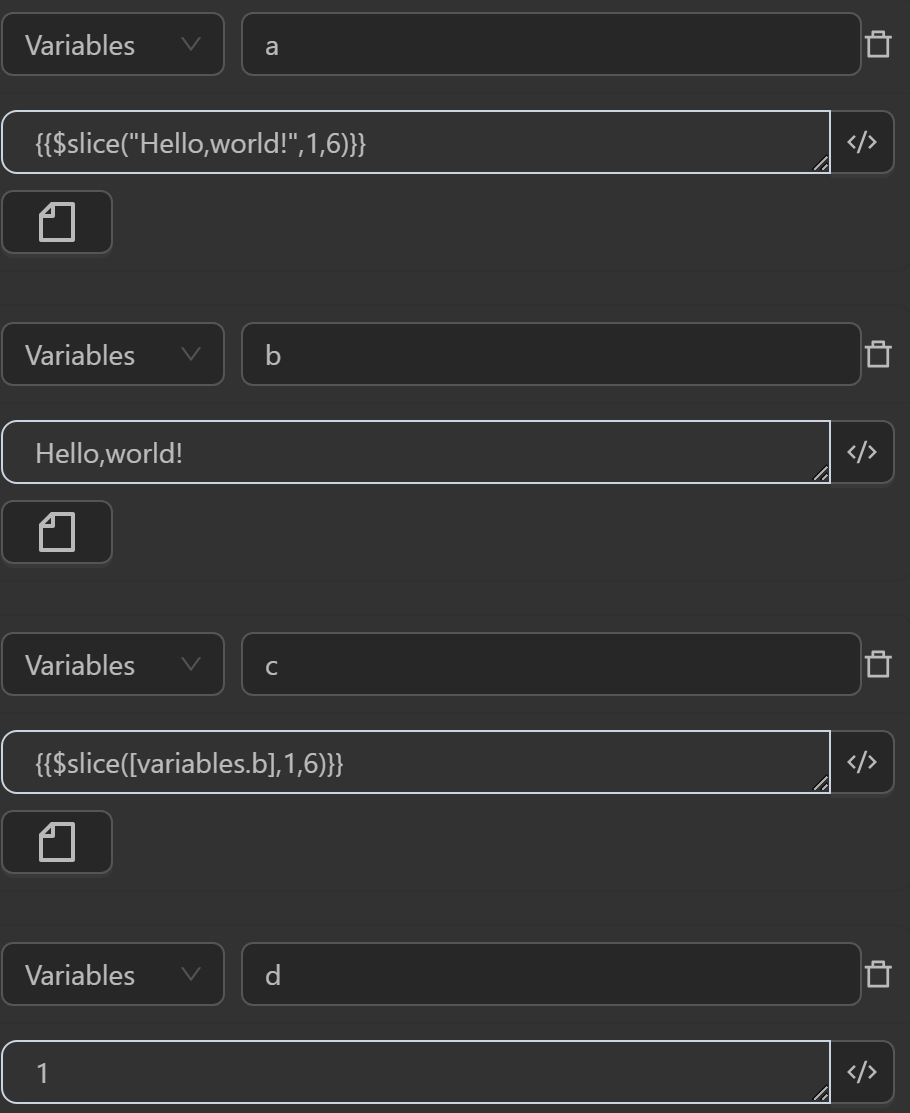
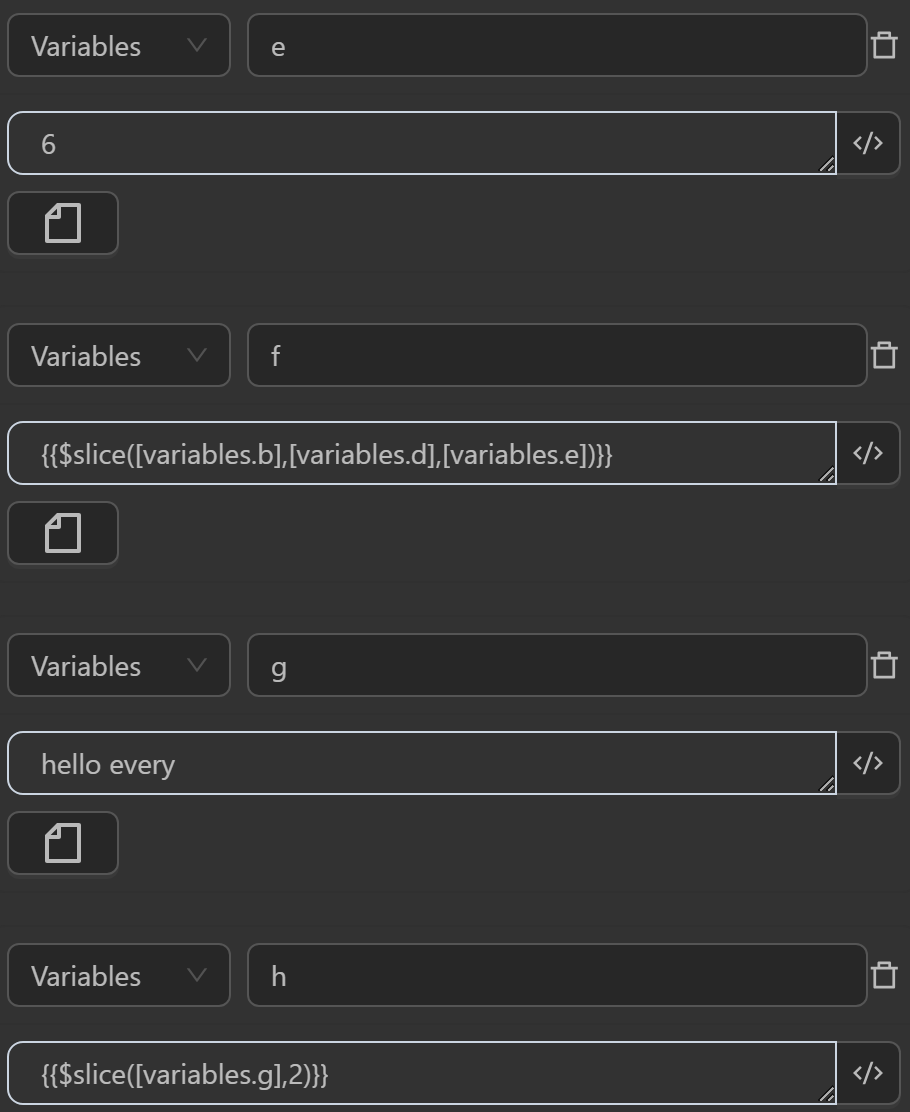
- The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression slices the stringHello,world!from position 1 to 6 - The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression slices the variablebcontaining the stringHello,world!from position 1 to 6 - The value assigned to the variable
fby the expression slices the variablebcontaining the stringHello,world!based on the desired range inserted into the variablesdas1andeas6, so the slicing range will be from1to6 - The value assigned to the variable
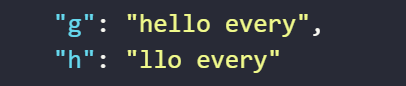
gby the expression slices the variablegcontaining the stringhello everyfrom the 2nd element position to the end of the string
The result returned will be as follows

$replace(value, search, replace)
The function first converts all parameters to strings. If the search parameter is a regular expression (i.e., starts and ends with slashes /), it creates a new RegExp object and uses it to replace matching substrings in the value string. Otherwise, it performs a simple string replacement. If the value string is empty, the function returns it immediately without performing any replacement.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
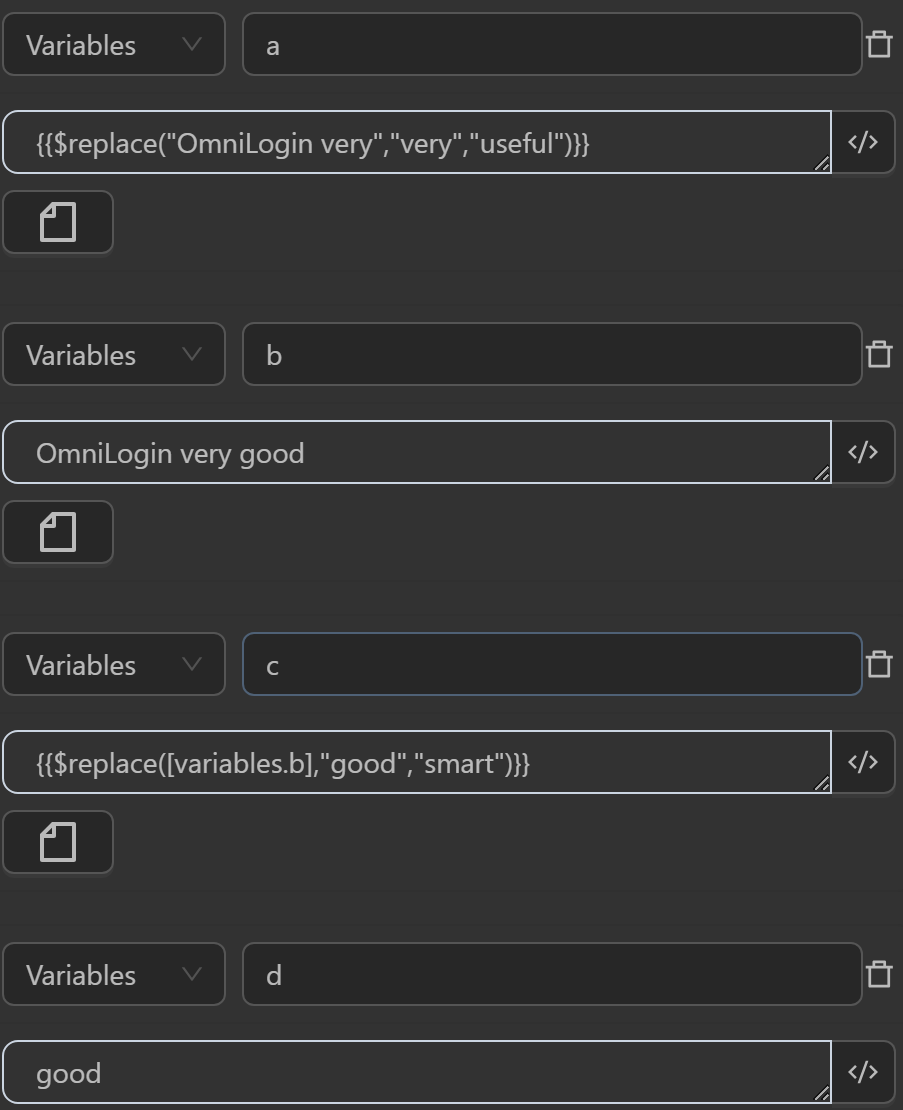
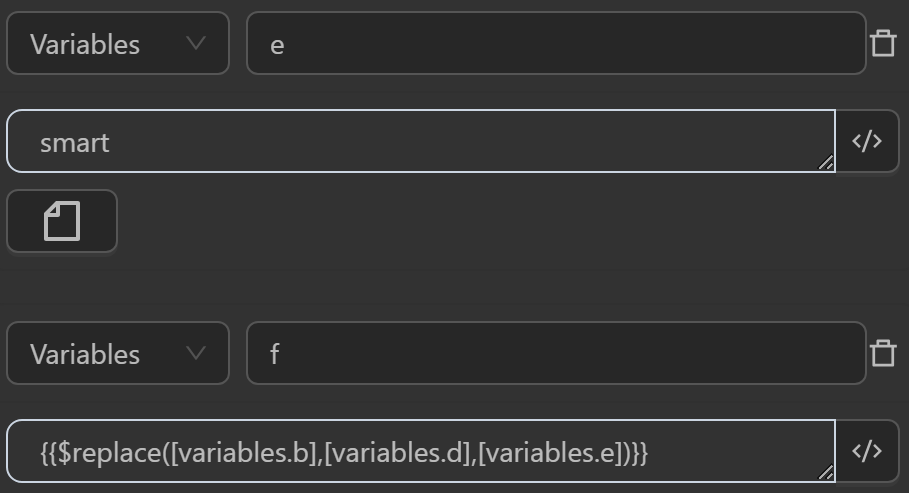
- The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression replaces the stringveryin the text with the input stringeasy to use - The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression replaces the substringgreatin the variablebcontaining the textOmniLogin very greatwith the input stringawesome - The value assigned to the variable
fby the expression replaces the substringgreatassigned to the variabledin a variablebcontaining the textOmniLogin very greatwith the stringawesomeassigned to the variable
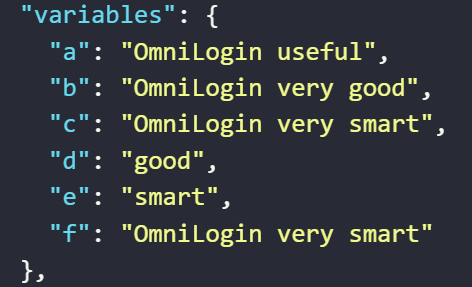
The result returned will be as follows
$replaceAll(value, search, replace)
This replaceAll function replaces all occurrences of the search string or regular expression in the value string with the replace string. It first checks if the search string is a regular expression (starts and ends with /) and creates a RegExp object if true. Then, it uses the replaceAll method to replace all occurrences of the search string or regular expression with the replace string. The function also converts the value, search, and replace parameters to strings if they are not strings to ensure the function works with non-string inputs.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
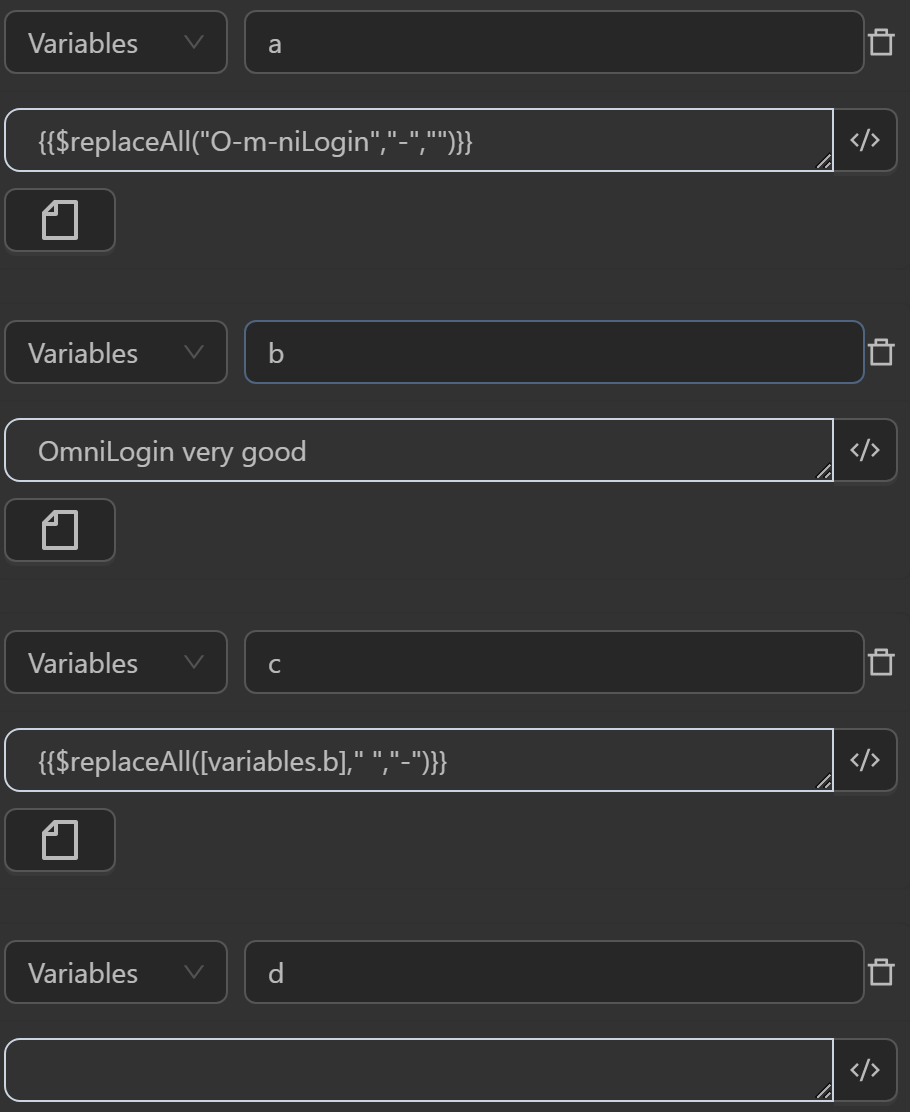
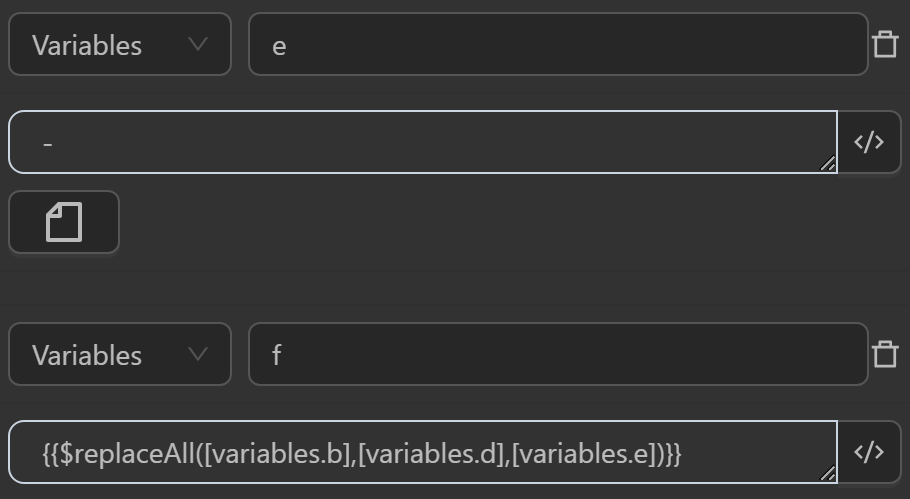
The result returned will be as follows
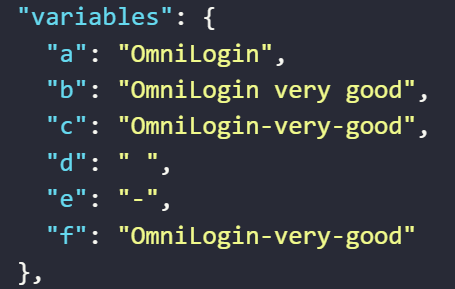
- The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression replaces all-characters in the stringO-m-niloginwith the""character - The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression replaces allcharacters in the string in the variablebcontaining the textOmniLogin very greatwith the input-character - The value assigned to the variable
fby the expression replaces allcharacters assigned to the variabledin a string assigned to the variablebcontaining the textOmniLogin very greatwith the-character assigned to the variablee
$toLowerCase(value)
This function converts a given value to lowercase. If the value is null or undefined, it returns the original value unchanged. Otherwise, it converts the value to a string and then to lowercase.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
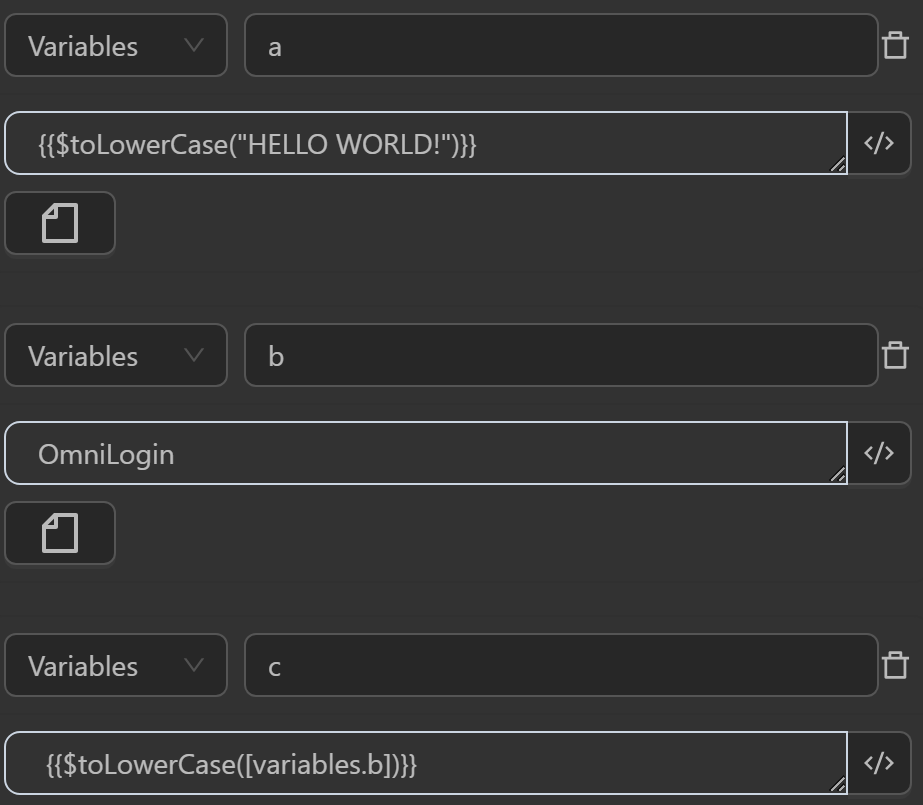
The result returned will be as follows
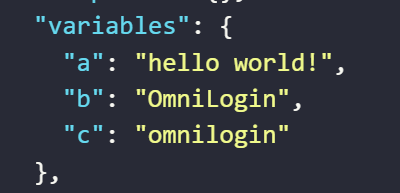
- The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression converts the stringHELLO WORLD!to the stringhello world! - The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression converts the stringOmniLoginassigned to the variablebto the stringomnilogin
$toUpperCase(value)
This function converts the input value to uppercase. If the value is falsy (e.g., null, undefined, empty string), it returns the original value unchanged. Otherwise, it converts the value to a string and returns the uppercase result.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
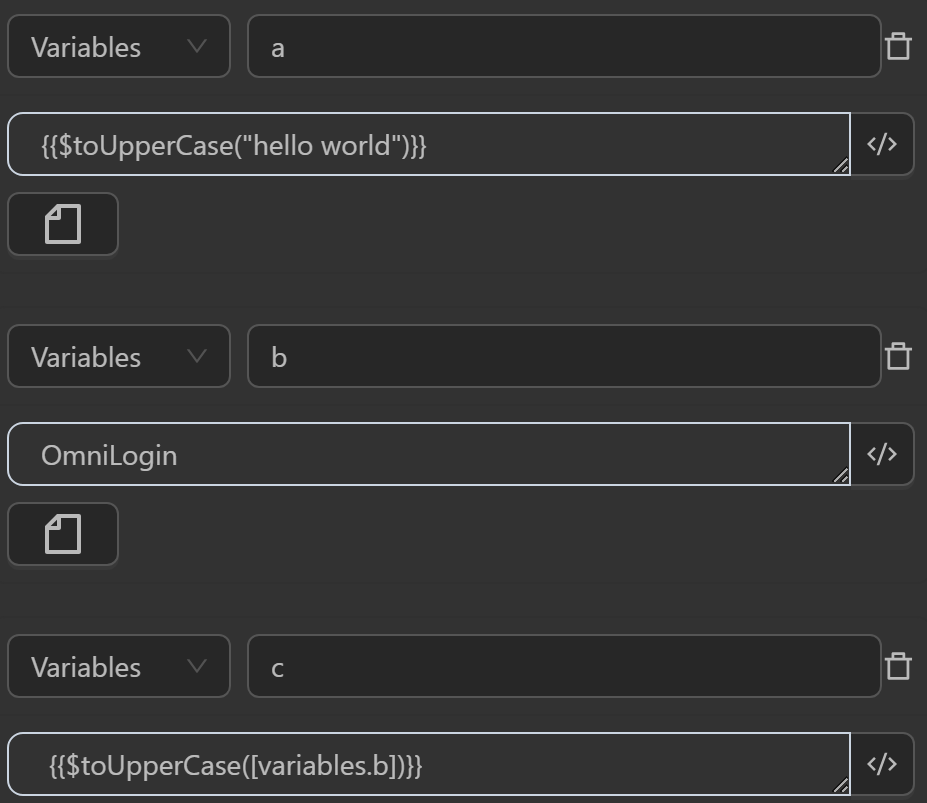
The result returned will be as follows
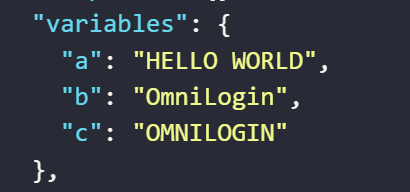
- The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression converts the stringhello worldto the stringHELLO WORLD - The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression converts the stringOmniLoginassigned to the variablebto the stringOMNILOGIN
$modulo(num, divisor)
This function calculates the remainder of num divided by divisor.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
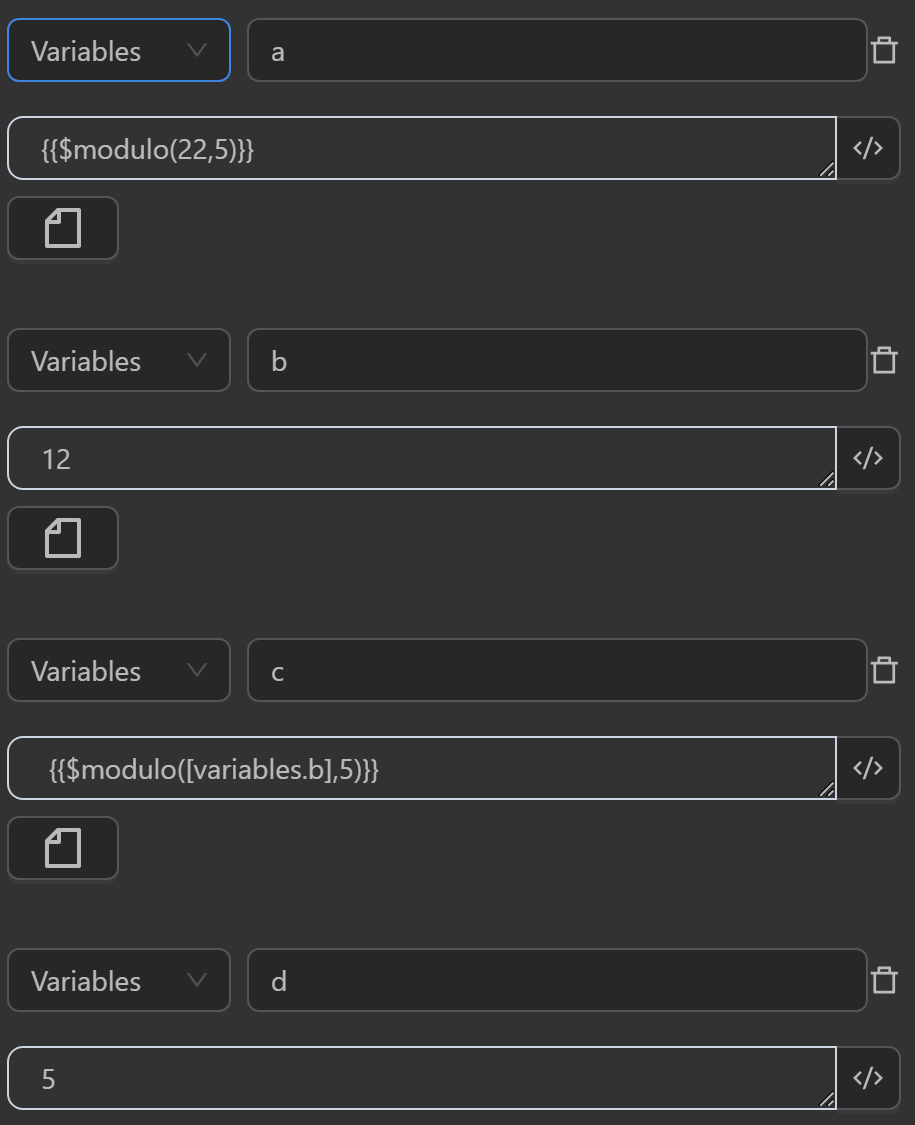
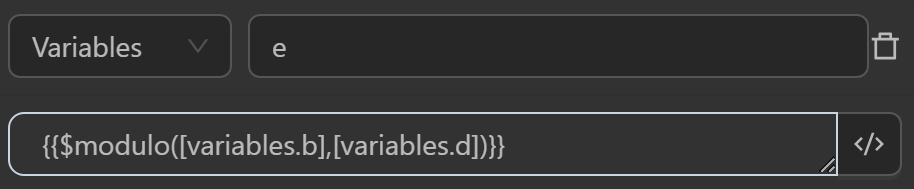
The result returned will be as follows
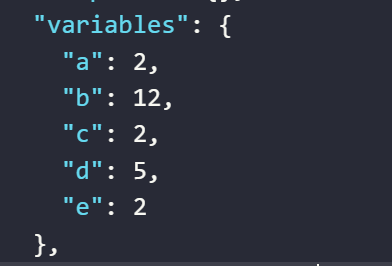
- The value assigned to the variable
aby the expression divides two numbers22and5to yield a remainder of2 - The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression divides two numbers12in the variableband5to yield a remainder of2 - The value assigned to the variable
eby the expression divides two numbers12in the variableband5in the variabledto yield a remainder of2
$filter(data, syntax)
This function filters data based on a JSONPath expression. If the input data is not an object or array, it returns the original data.
data: JavaScript object to querysyntax: JSONPath Syntax
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
First, create an array of multiple objects in the JavaScript Code node, then assign that array to a variable for use outside the workflow using the omniloginSetVariable function
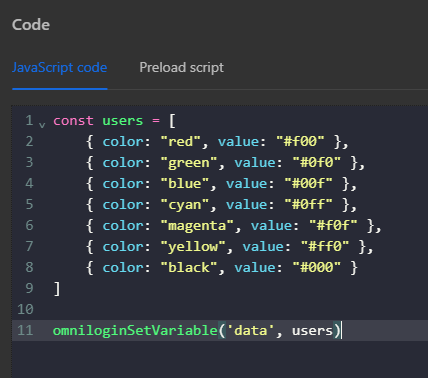
Then use the expression {{$filter([variables.data],'$..color')}} in the Write Log node. When using this expression, the function will retrieve all values of the color key in the data variable
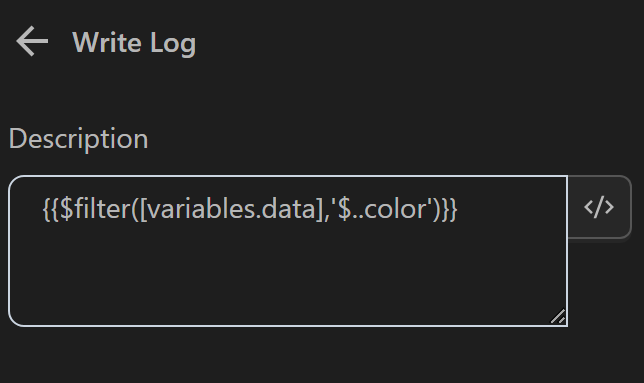
The result returned will be as follows

$reverse(value)
This reverse function takes a value and reverses the order of its elements. If value is not an array or object, the function returns the original value unchanged.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
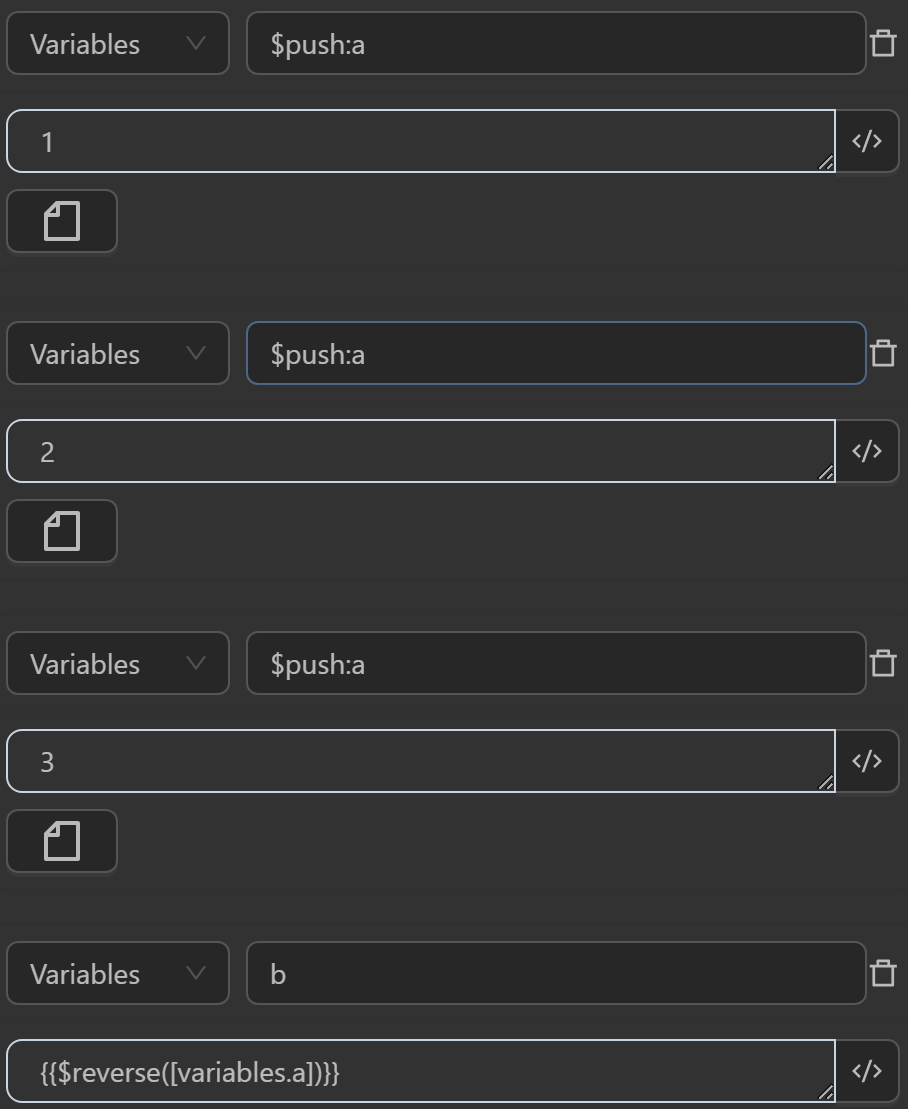
The result returned will be as follows
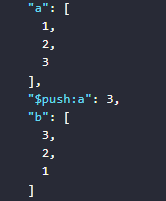
- First, assign three values to the variable
ato make it an array containing three values1,2,3 - The value assigned to the variable
bby the expression reverses the order of elements in the variablea
$shuffle(value)
This shuffle function takes an array value and returns a new array with its elements randomly arranged.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
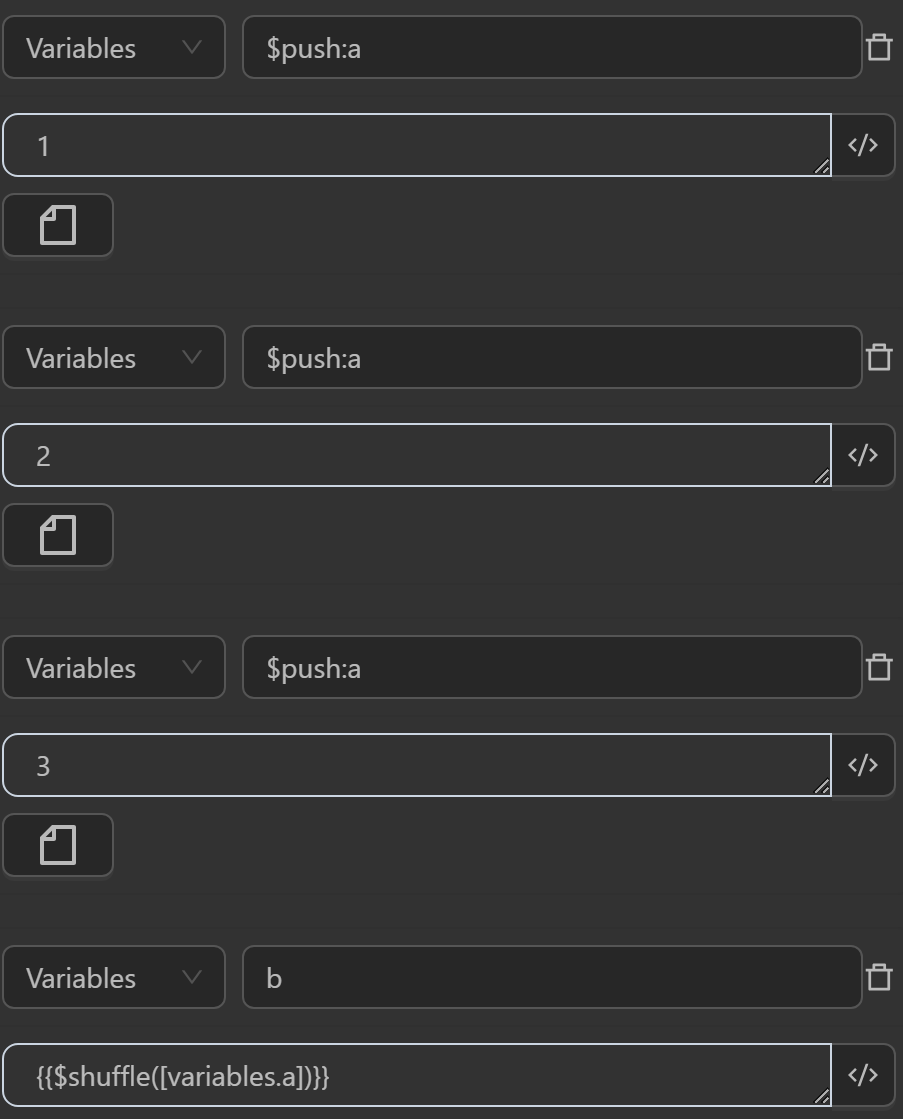
The result returned will be as follows
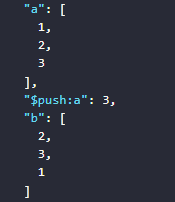
- First, assign three values to the variable
ato make it an array containing three values1,2,3 - The value assigned to the variable
bby the expression shuffles the order of elements in the variablea
$includes(data, item)
The includes function checks whether an item exists in a dataset data. If data is an array, the function uses the built-in includes() method to check for the existence of item. If data is not an array, the function returns false immediately.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
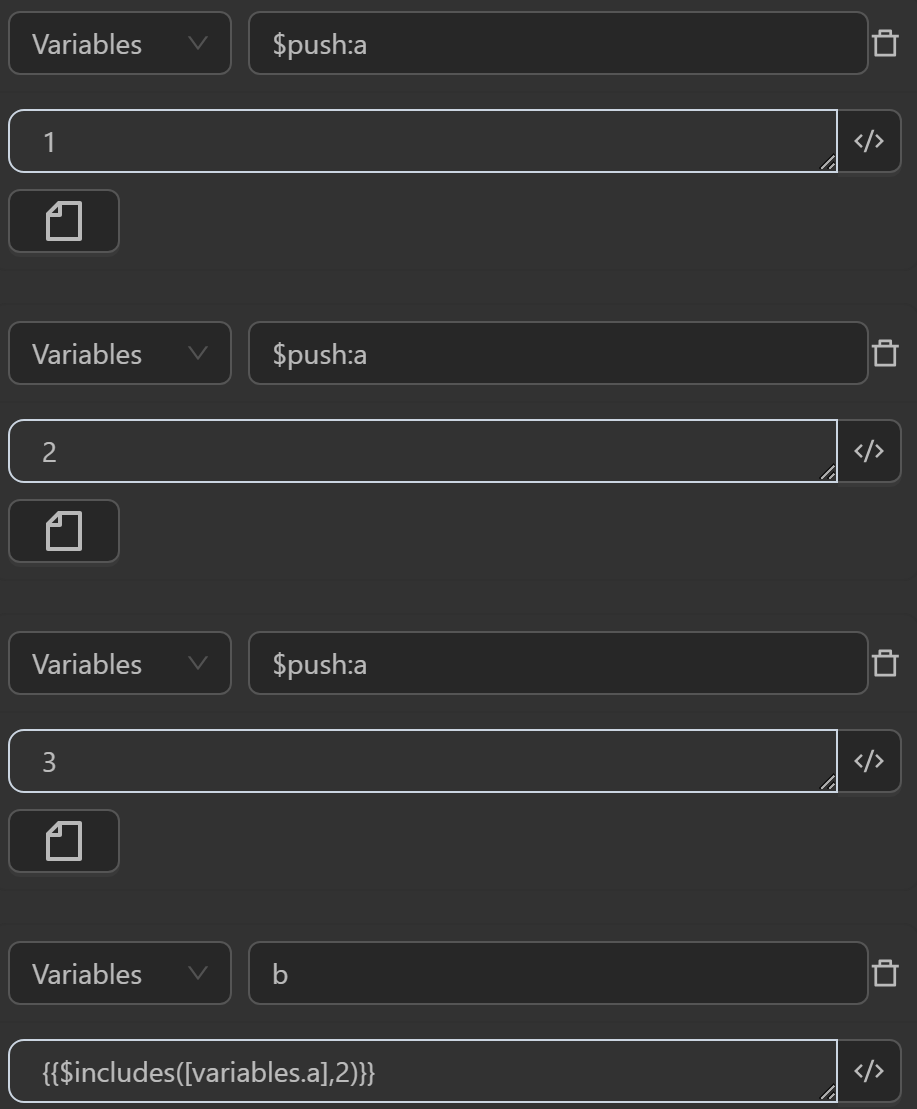
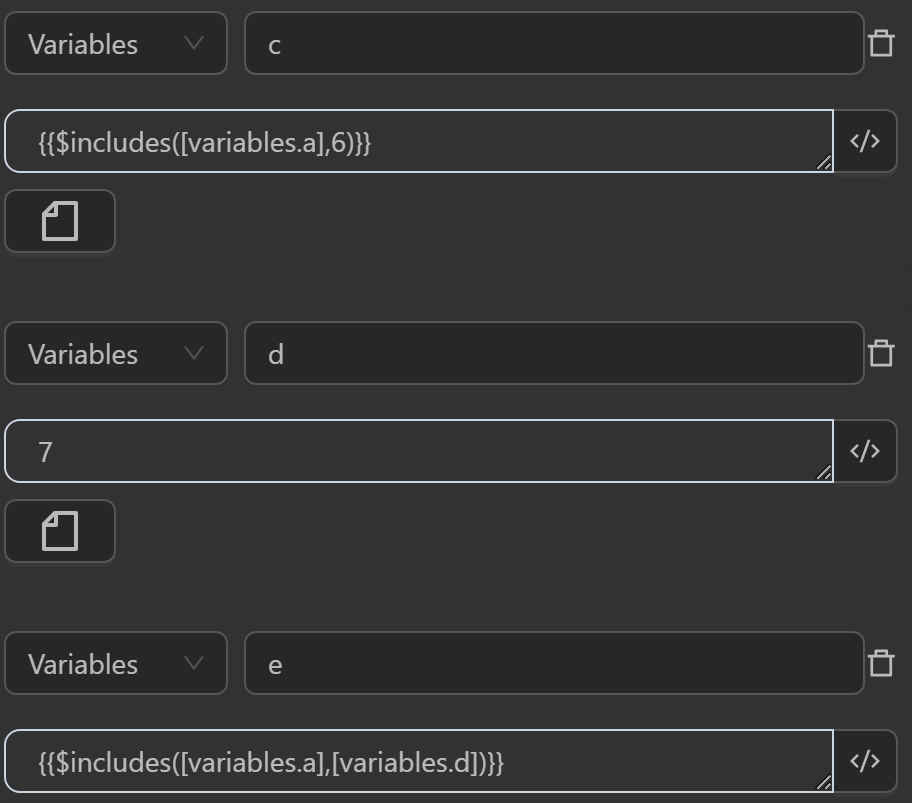
The result returned will be as follows
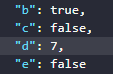
- First, assign three values to the variable
ato make it an array containing three values1,2,3 - The value assigned to the variable
bby the expression checks whether the number2is in theaarray, returningtrue, meaning the number2is in theaarray - The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression checks whether the number6is in theaarray, returningfalse, meaning the number6is not in theaarray - The value assigned to the variable
eby the expression checks whether the number7assigned to the variabledis in theaarray, returningfalse, meaning the number7is not in theaarray
$trim(data)
This trim function takes a data value and returns it after removing whitespace from the beginning and end. If data is not a text string, the function converts it to a string before removing whitespace.
Example
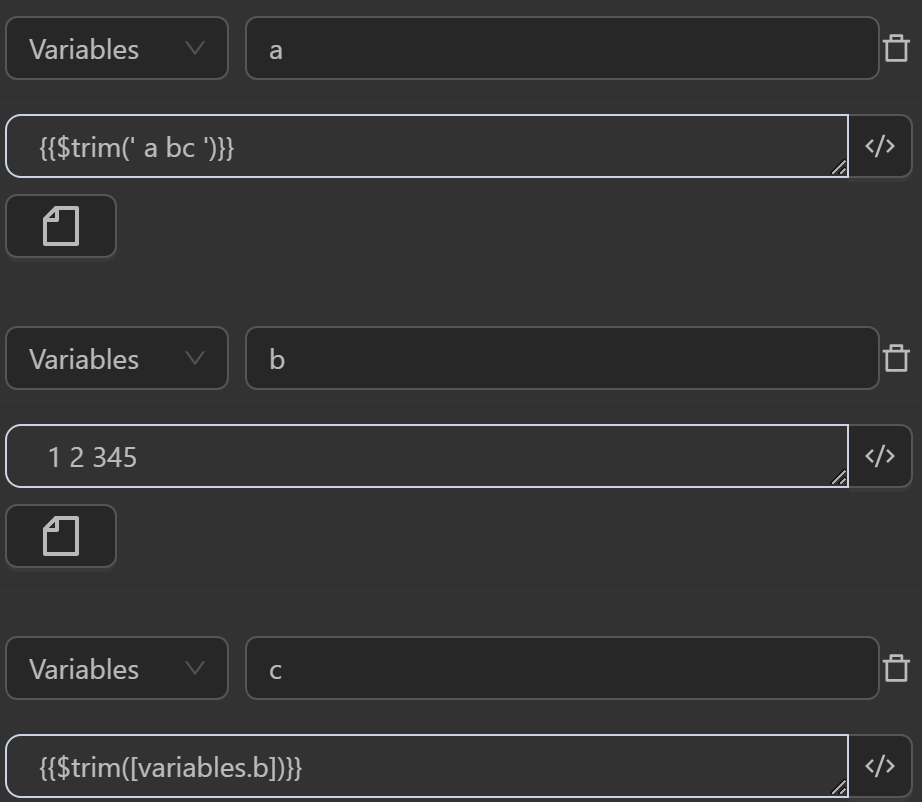
You can use the function in cases like the following.
The result returned will be as follows
- The value assigned to the variable
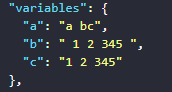
aby the expression removes whitespace from the texta bcwritten in thetrimfunction, so the variableawill receive the stringa bcafter removing whitespace from the beginning and end - The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression removes whitespace from the text1 2 345assigned to the variablebwritten in thetrimfunction, so the variablecwill receive the string1 2 3 45after removing whitespace from the beginning and end
$match(value, regex, index, flags)
This match function performs a search and returns the matching result of a regular expression regex in a text string value. The function has the following parameters:
- value: The text string to search
- regex: The regular expression to search for
- index: The index of the match result to return (optional, defaults to -1)
- flags: Optional flags for the regular expression (optional, defaults to empty)
The function will return:
- The full match result as a string if index is not specified
- The match result at the specified index if index is specified
- An empty string if no match is found
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
The result returned will be as follows

- The value assigned to the variable
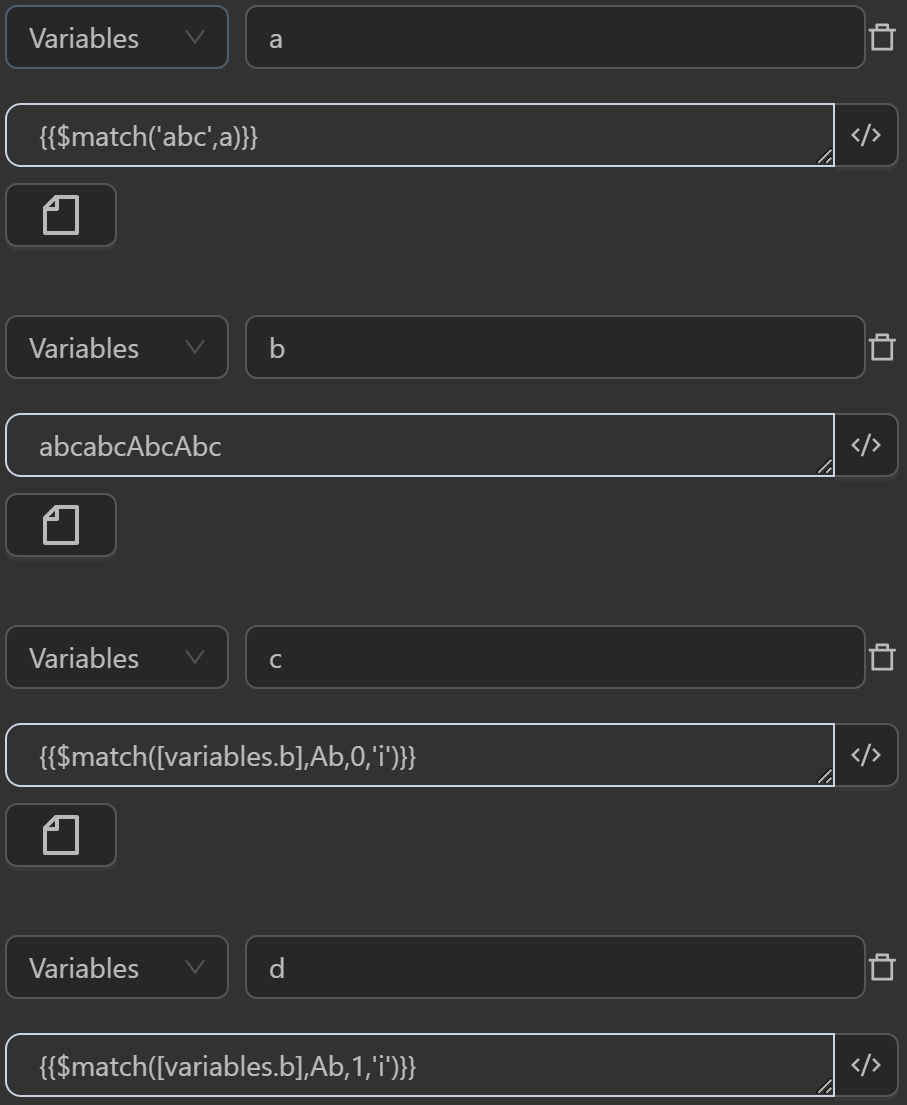
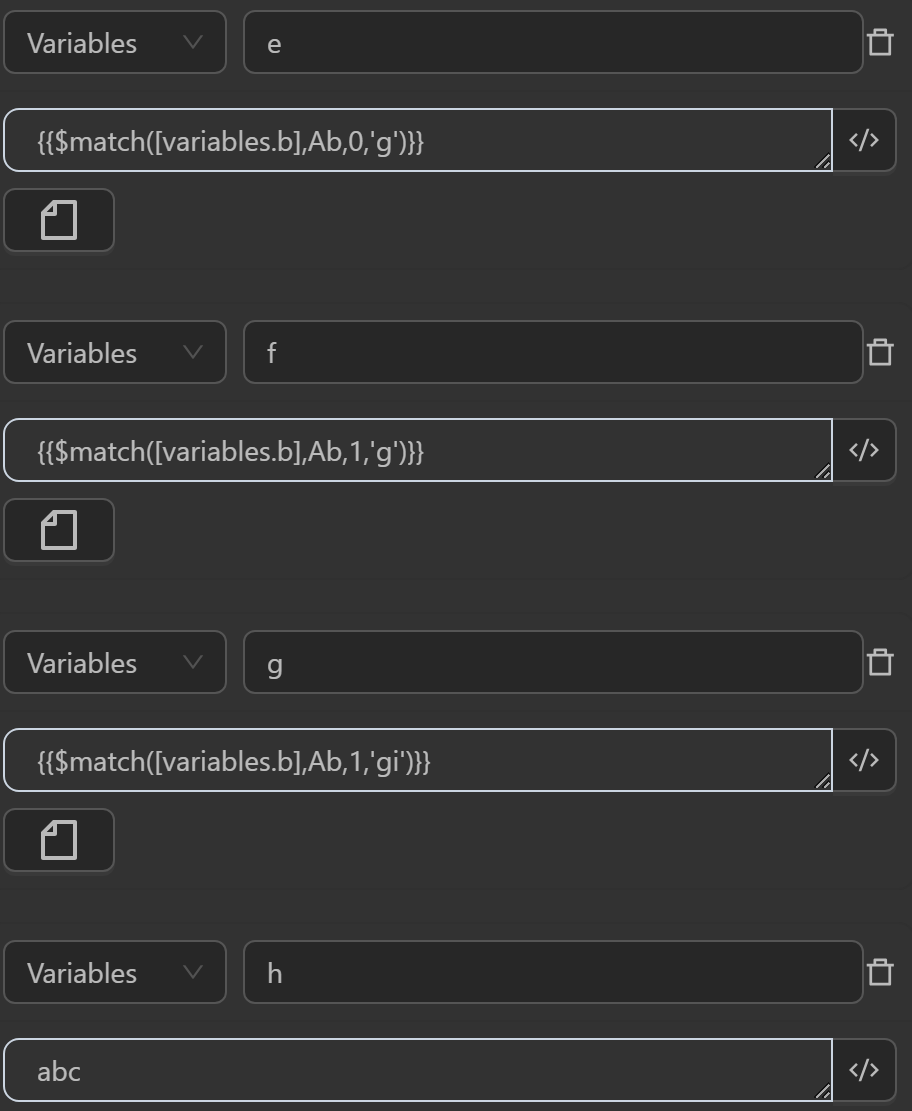
aby the expression searches the stringabcand returns the text segment matching the regular expressiona - The value assigned to the variable
cby the expression searches the stringabcabcAbcAbcassigned to the variableband returns the text segment matching the regular expressionAb. Using regexFlags asimeans case-insensitive text. Index as0means taking the first element matching the regular expression if there are multiple matching texts. Thus, the result retrieves the text segmentabinstead ofAbas in the regular expression - The value assigned to the variable
dby the expression searches the stringabcabcAbcAbcassigned to the variableband returns the text segment matching the regular expressionAb. Using regexFlags asimeans case-insensitive text. Index as1means taking the second element matching the regular expression if there are multiple matching texts. Thus, the result retrieves the text segmentundefinedinstead ofAbas in the regular expression because theiflag only takes the first element - The value assigned to the variable
eby the expression searches the stringabcabcAbcAbcassigned to the variableband returns the text segment matching the regular expressionAb. Using regexFlags asgmeans taking all elements matching the regular expression and case-sensitive. Index as0means taking the first element matching the regular expression if there are multiple matching texts. Thus, the result retrieves the text segmentAbasAbas in the regular expression - The value assigned to the variable
fby the expression searches the stringabcabcAbcAbcassigned to the variableband returns the text segment matching the regular expressionAb. Using regexFlags asgmeans taking all elements matching the regular expression and case-sensitive. Index as1means taking the second element matching the regular expression if there are multiple matching texts. Thus, the result retrieves the text segmentAbasAbas in the regular expression because thegflag returns a list of texts ["Ab","Ab"] - The value assigned to the variable
gby the expression searches the stringabcabcAbcAbcassigned to the variableband returns the text segment matching the regular expressionAb. Using regexFlags asgmeans taking all elements matching the regular expression and case-sensitive. Index as1means taking the second element matching the regular expression if there are multiple matching texts. Thus, the result retrieves the text segmentabinstead ofAbas in the regular expression because thegiflags return a case-insensitive list of texts ["ab","ab","Ab","Ab"] - The value assigned to the variable
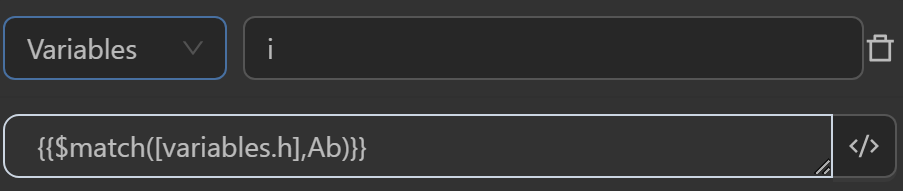
iby the expression searches the stringabcassigned to the variablehand returns the text segment matching the regular expressionAb. Thus, the result retrieves the text segment""instead ofAbas in the regular expression because there are no flags, so it is case-sensitive, and the string does not contain text matching the regular expression
$join(data,sep=" ")
This join function concatenates an array of values into a single string, using a specified delimiter. If no delimiter is provided, it defaults to a space. If the input is not an array or is invalid, it returns the original value.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
The result returned will be as follows

- The value assigned to the variable
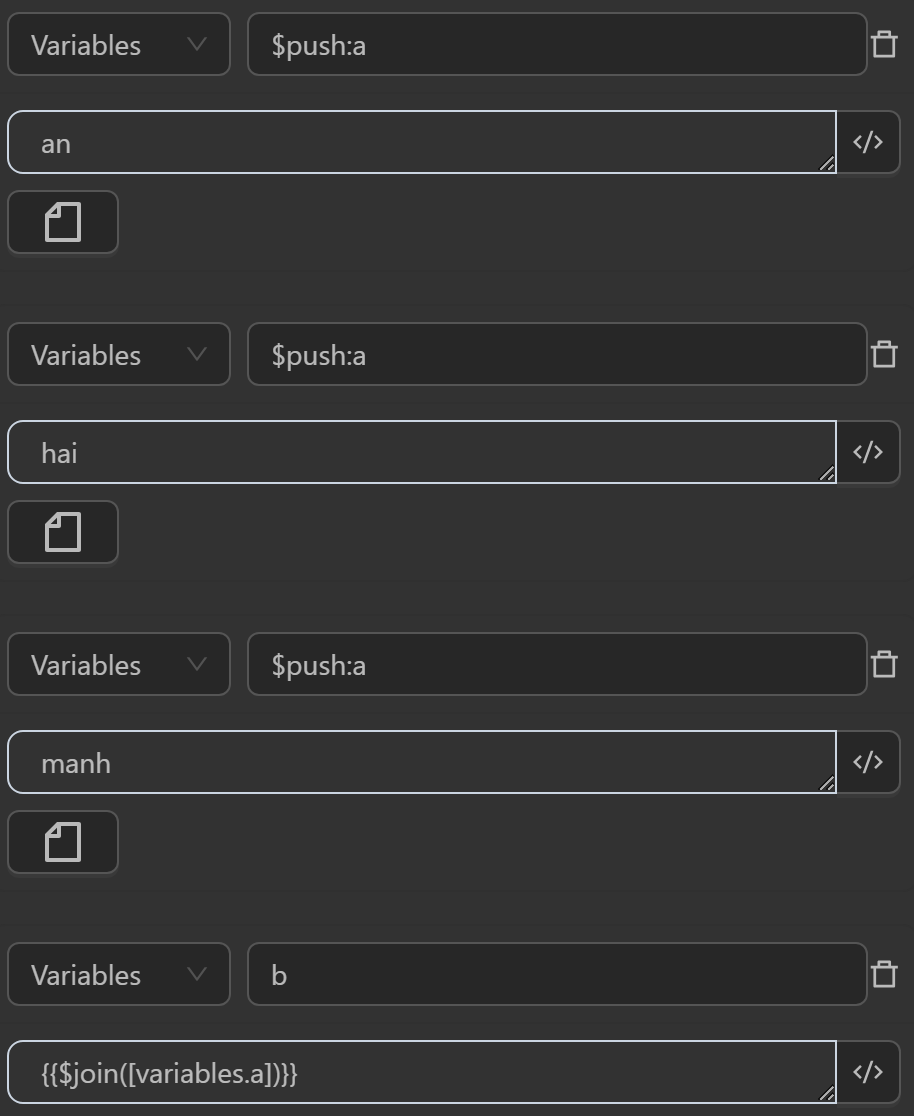
aby the expression converts a variable into an array to contain multiple elements - The value assigned to the variable
bby the expression joins theaarray into a new string. Since there is nosep, the elements in the string are separated by a default space - The value assigned to the variable
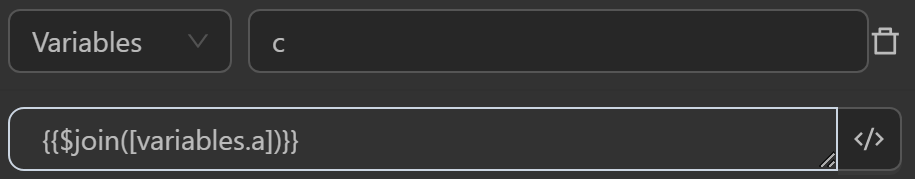
cby the expression joins theaarray into a new string. Since there issep="-", the elements in the string are separated by a-delimiter
Example when using the Set Cookie function of the Cookie node
Here you will use a JSON file to import cookies into the desired profile.
This is the profile before importing cookies
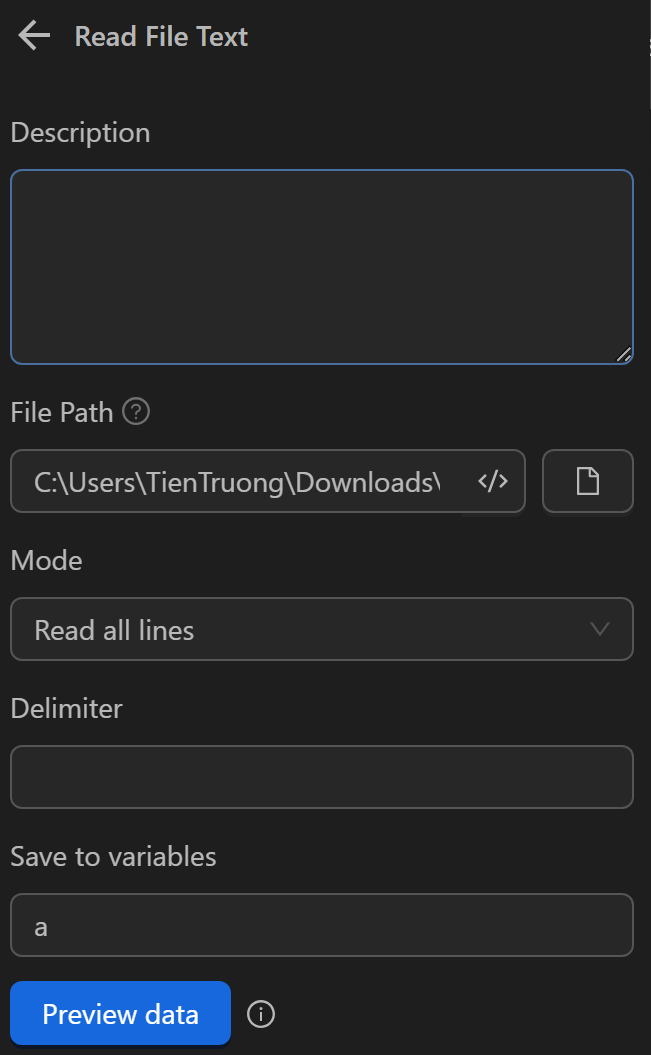
First, you will use the Read File Text node to read the JSON file containing cookies. To use that data in subsequent steps, you will assign it to a variable named a
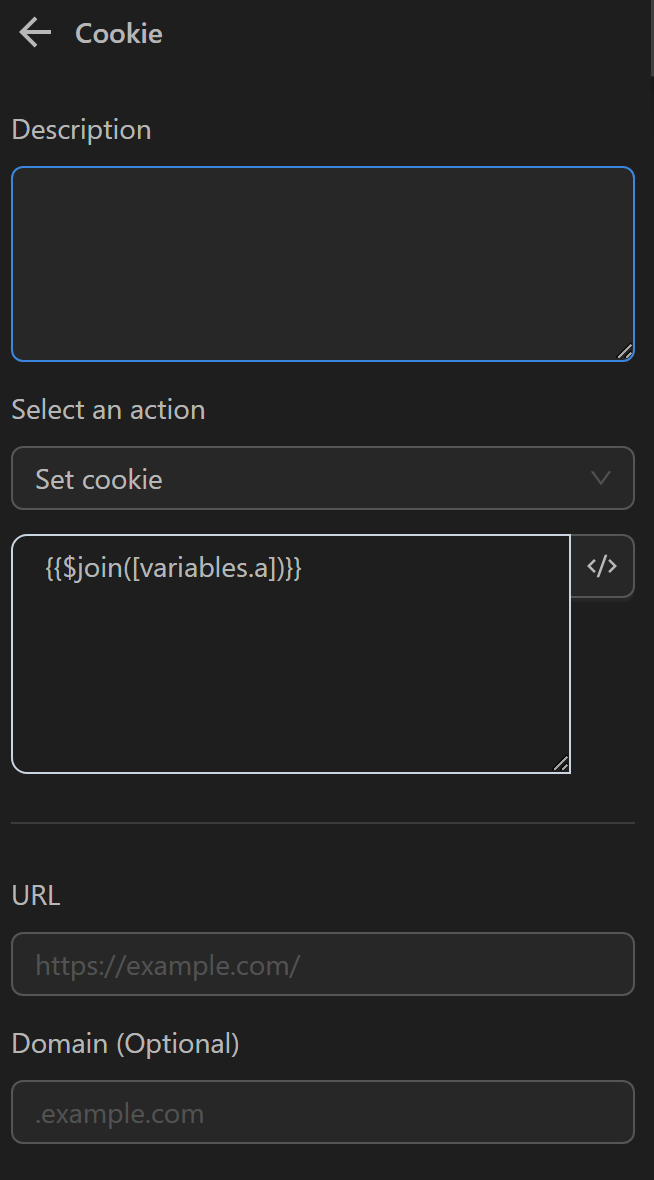
Then, you will use the Cookie node with the Set Cookie option to import the cookie values read from the file. In the value input section, you will use the expression {{$join([variables.a])}} to convert the data from multiple lines into a single line (since using the Read File Text node converts the data into multi-line text)
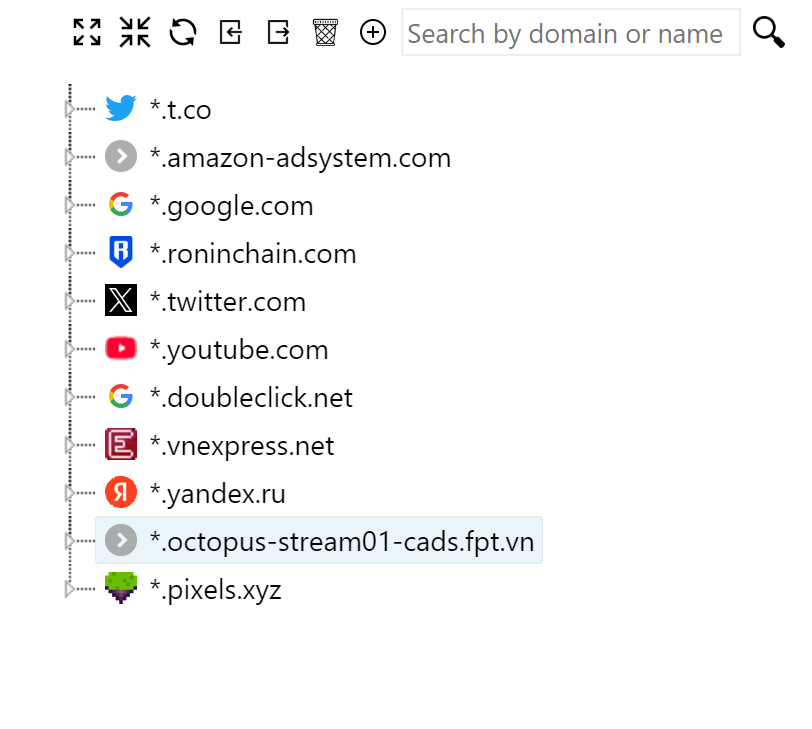
After running, your cookies will be added to the profile
$find(data, path, value)
This function searches for a single value in a nested object or array data, based on a specified path.
Here is a description of the values in the function
pathis a string of keys for the values- The function iterates through each key in the
path, accessing the corresponding property in the object or arraydata. - If the current property is an array, it uses the key as an index; otherwise, it uses the key as a property name.
- The function returns the first value matching the specified
value, or an empty string if no match is found.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
Here you will create an array containing objects in the JavaScript Code node, then assign that array’s value outside the workflow for use with the omniloginSetVariable formula
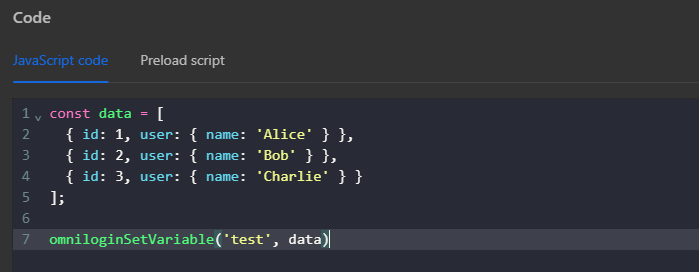
Then use the expression {{$find([variables.test],'user.name','Alice')}} in the Write Log node to log the search result using the find function. Here you use the expression user.name corresponding to path because the name value, you are searching for is within the user object. If you replace user with name along with the valueyou only need to specify name. The value Alice corresponds to value
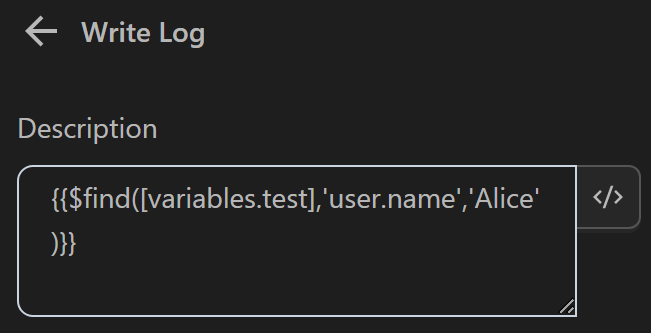
The result returned will be as follows

- The value printed in the
Write Lognode by thefindfunction with the expression searching fornameasAlicein thetestvariable containing an array. The function returns the first object matching the condition
$findAll(data, path, value)
This is a function that filters an object or array data to find all elements matching a value at a specific path.
Here is a description of the values in the function
- If
datais not an object or array, return it as is. - Split the
pathinto individual keys using dots. - Iterate through each key in the path and navigate through the corresponding object or array
data. - If the current value is an object or array, use the key to access its property or element.
- If the current value is an array, use the key as an index to access its element.
- If the final value matches the
valueparameter, include it in the filtered result. - Return the filtered result as an array. If no matches are found, return an empty array.
Example
You can use the function in cases like the following.
Here you will create an array containing objects in the JavaScript Code node, then assign that array’s value outside the workflow for use with the omniloginSetVariable formula
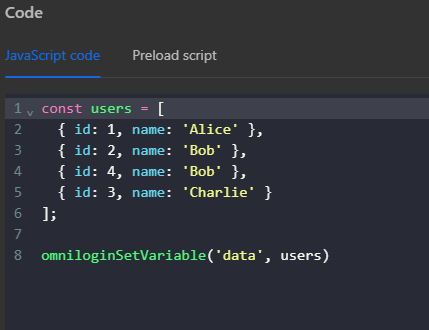
Then use the expression {{$findAll([variables.data], 'name','Bob')}} in the Write Log node to log the search result using the find function. Here you use the expression name corresponding to path, and the value Bob corresponding to value

The result returned will be as follows

- The values printed in the
Write Lognode by thefindAllfunction with the expression searching fornameasBobin thedatavariable containing an array. The function returns all objects matching the condition
$stringify(value)
It is used to convert a JavaScript object or value into a JSON string. The main purpose is to "package" the data, making it easy to send over the network.
Example
For instance, a user might want to send data from the b variable to a Google Sheet via an API using the HTTP Request node.
First, go to the link https://script.google.com/home and follow the steps as shown in the images:

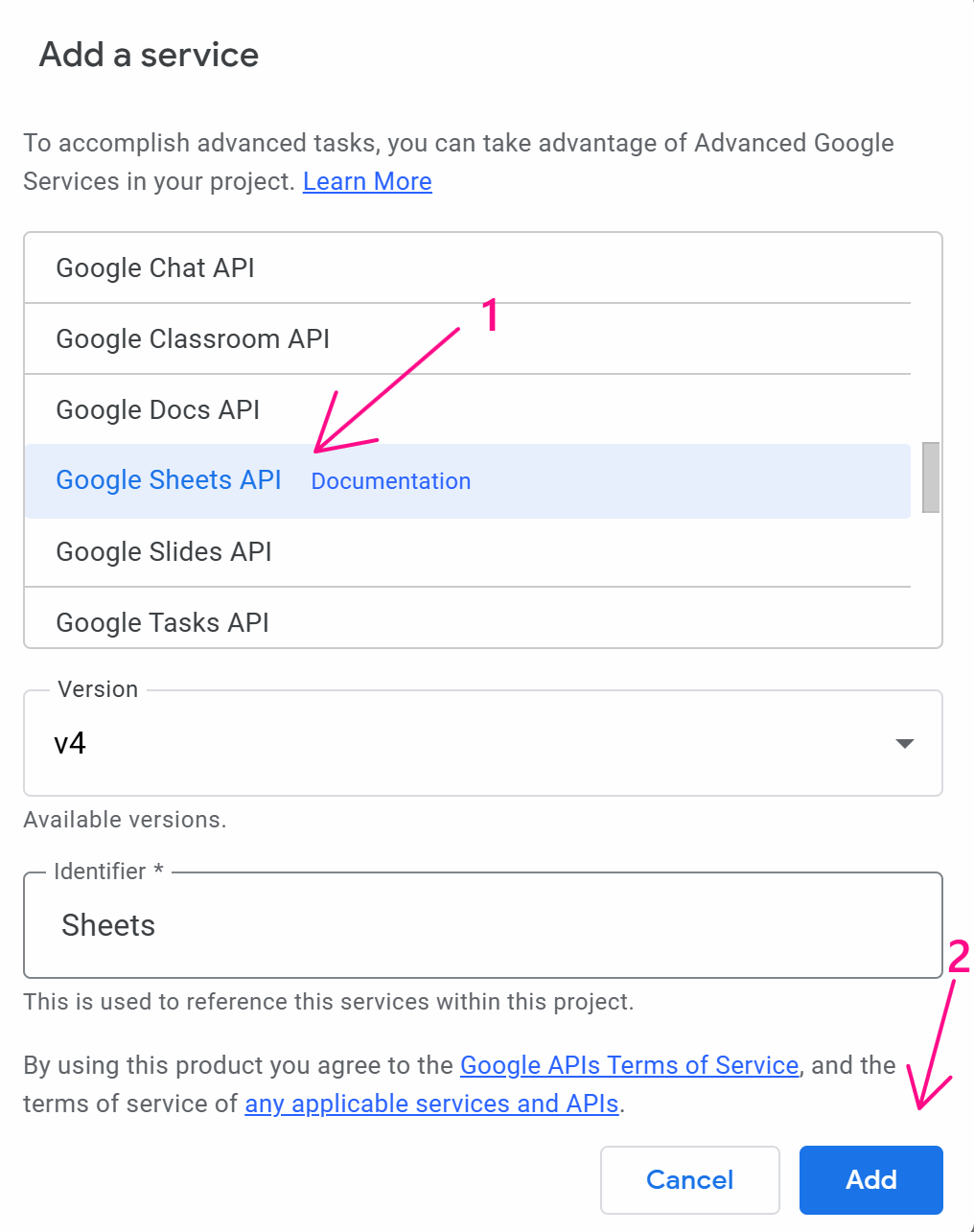
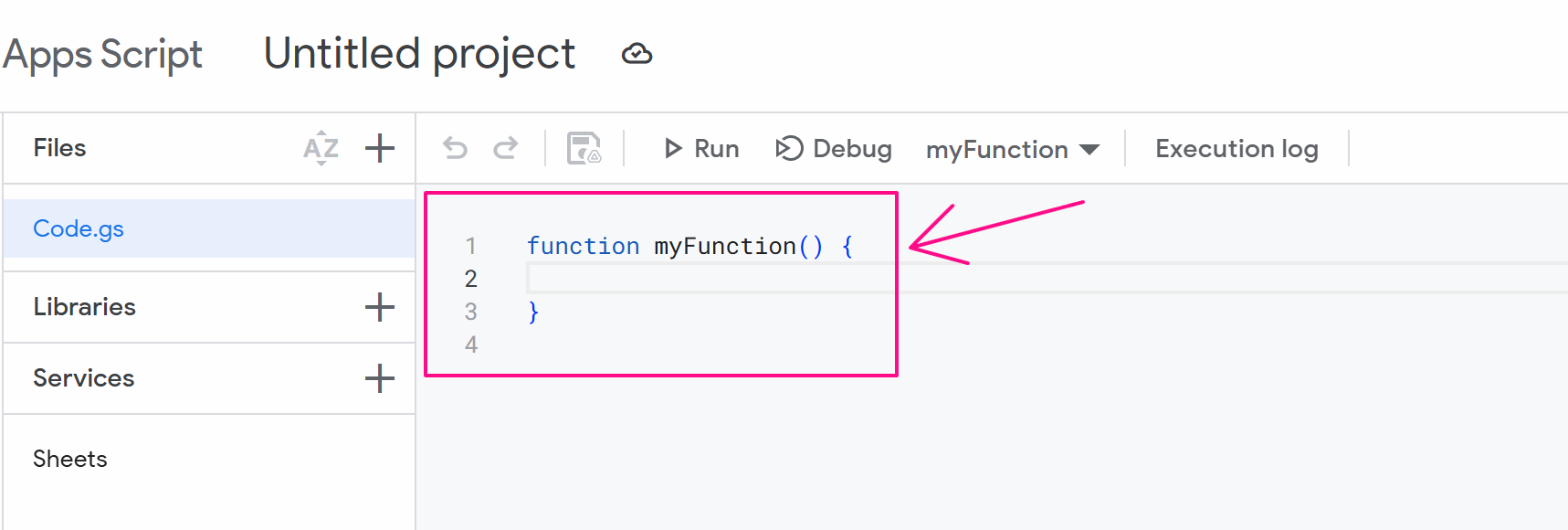
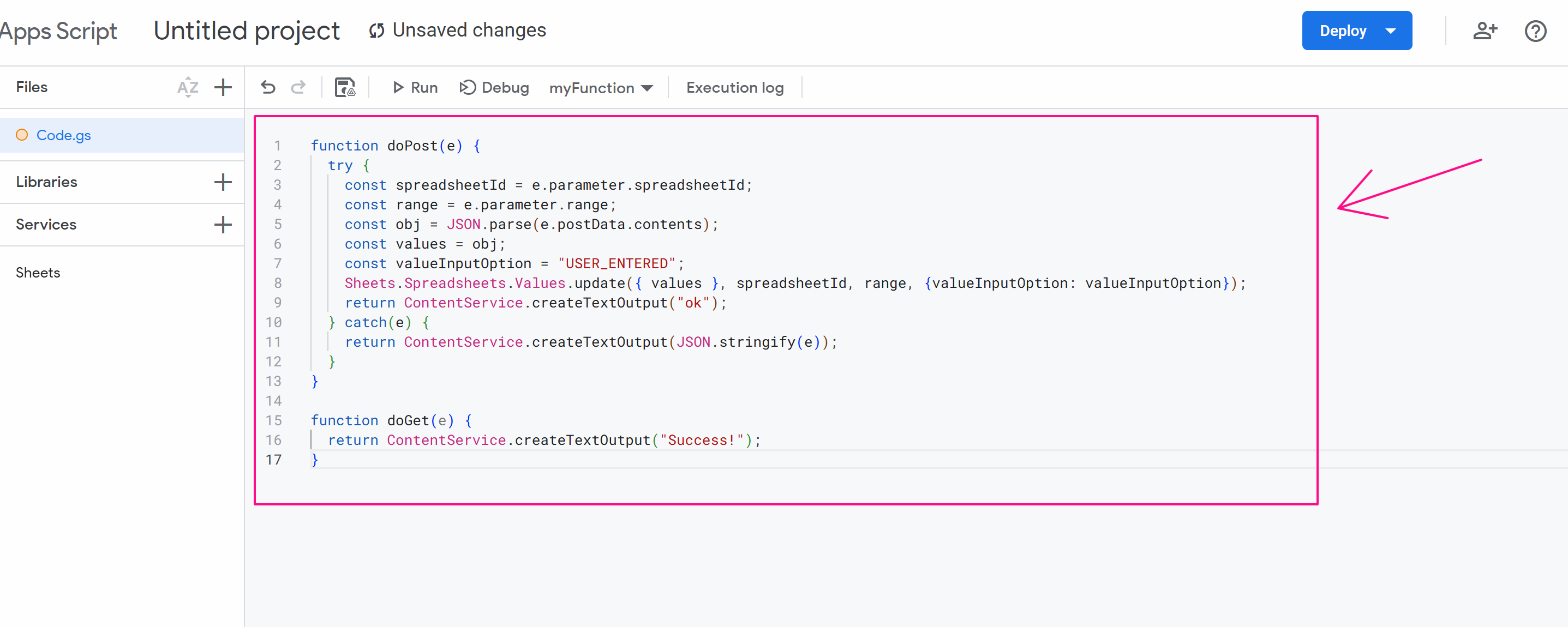
At this point, you delete the existing value and paste this code:
function doPost(e) {
try {
const spreadsheetId = e.parameter.spreadsheetId;
const range = e.parameter.range;
const obj = JSON.parse(e.postData.contents);
const values = obj;
const valueInputOption = "USER_ENTERED";
Sheets.Spreadsheets.Values.update({ values }, spreadsheetId, range, {valueInputOption: valueInputOption});
return ContentService.createTextOutput("ok");
} catch(e) {
return ContentService.createTextOutput(JSON.stringify(e));
}
}
function doGet(e) {
return ContentService.createTextOutput("Success!");
}

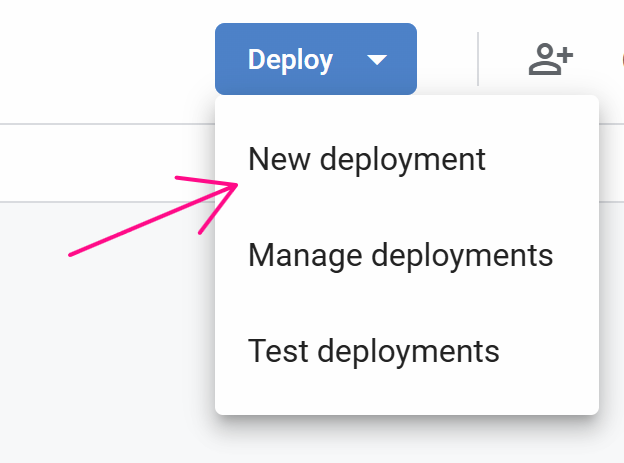
Finally, copy this URL value:
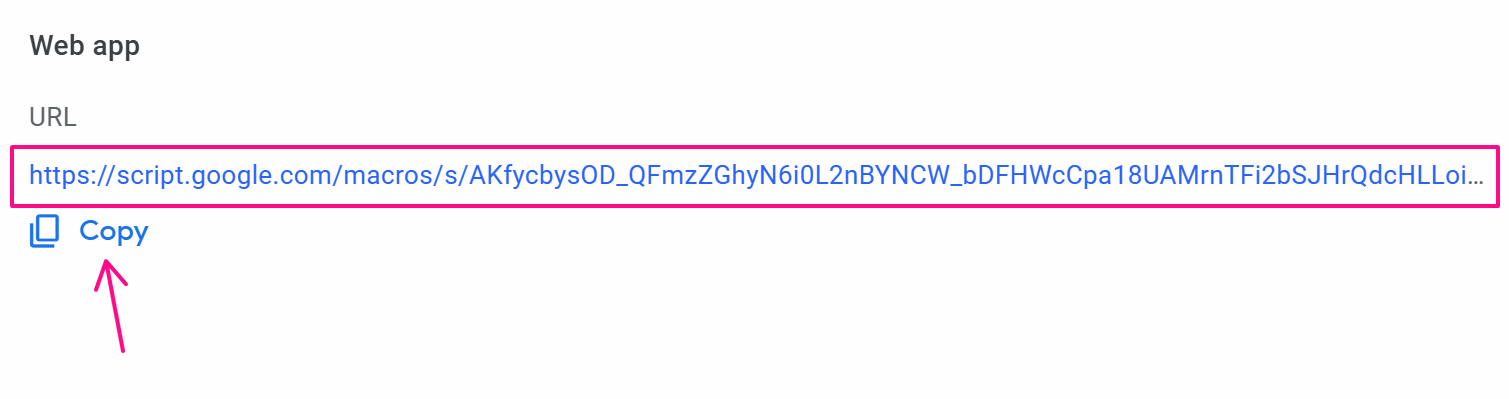
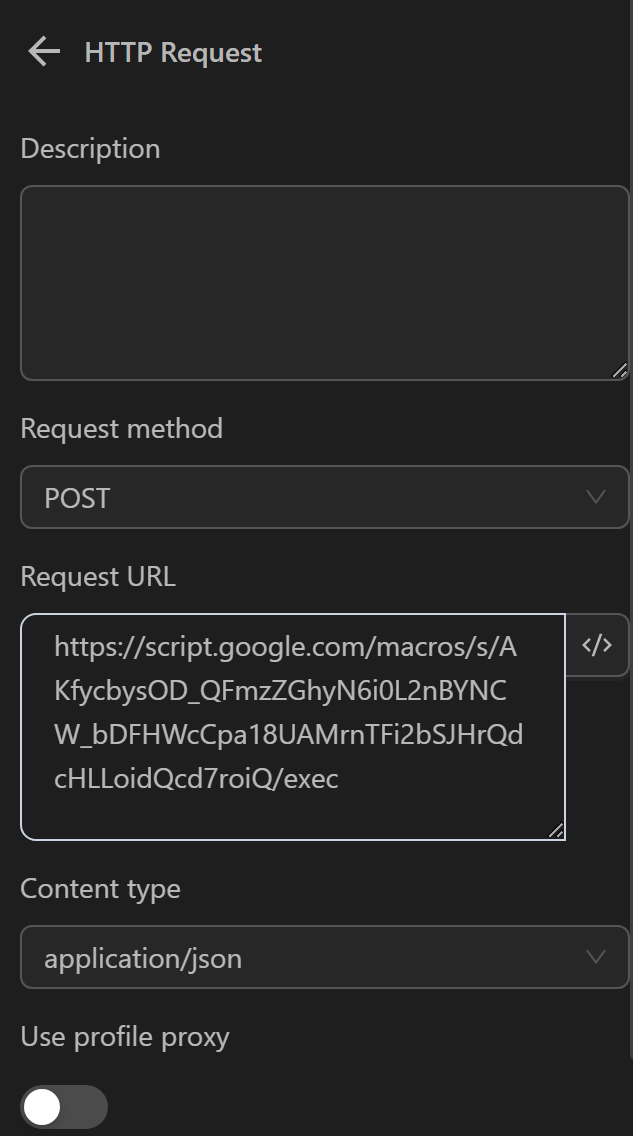
Now, you will use this URL in the HTTP Request node as follows:
In the Request URL, you will fill in according to the formula URL?googlesheetId=a&range=b, where a is the ID of the Google Sheets where you want to insert the status, and b is the cell, you want to update the value for. If there are multiple sheets like sheet1, sheet2, you can specify the range as range=sheet2!b. In this case, it would be written as: https://script.google.com/macros/s/AKfycbxw6yFtbqapqJ07J9gwyKUoGhXjc_kIehxT1HPO9ZUwCal-iw4SIjB53ahIs-WNEBXdtA/exec?spreadsheetId=1qDb4fe4dWFHfd1HIYkc8JPTd0IoYpsRVyTwfJhaZcV8&range=A1.
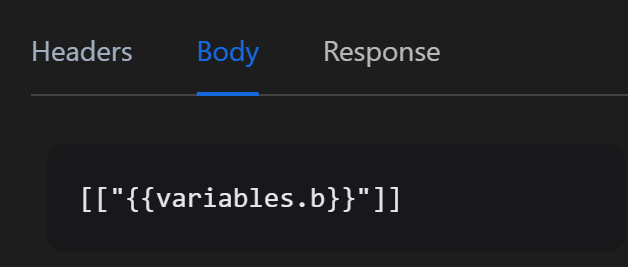
Typically, in the content field, a user enters the text they wish to insert. To use a variable or a value from any expression, they can write it as follows: [["{{variables.b}}"]] to insert the value of the b variable into a column.
However, the stringify function can also be applied as follows:
[[{{$stringify([variables.b])}}]]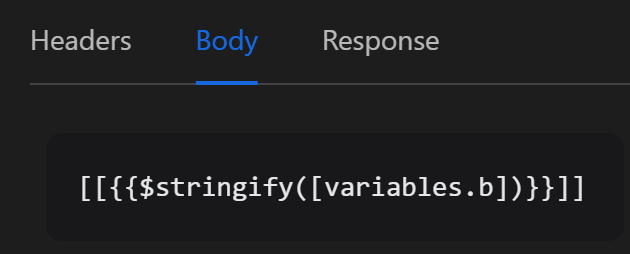
In the Response section, the user assigns the response value to a status variable to determine if the insertion was successful.
If the insertion is successful, the variable receives the following value: